Top 12 Psychological Pricing Strategies To Convince Customers

You may have a winning product catalog, however, that’s not enough to convince your customers.
Because customers are not easy, and all the store owners nod along to it.
That’s why sales & marketing teams constantly search for appealing offers to target buyers. One of the strategies they use is “psychological pricing strategies”.
It’s about putting your product prices in a way that makes your customers perceive your product/service as affordable and valuable.
And yeah, it’s not about tricking customers — far from it.
In this blog, we’ll open up all the necessary information you might need to successfully set up psychological pricing for your product catalog.
The discussion will revolve around the following areas.
- What Is Psychological Pricing
- Why It’s Necessary
- 12 Best Tactics & Strategies
- Its Advantages & Disadvantages
- Best Practices To Follow
… and more.
So, are you ready to turn your browsers into buyers? Let’s get into it.
What Is Psychological Pricing?
Psychological pricing is a pricing strategy that uses various tactics to manipulate customers’ purchase decisions, making them perceive a product or service as more affordable, attractive, and valuable. These pricing tactics trigger emotional or psychological responses in customers, rather than just logical ones.
This pricing strategy is something that we all have anticipated while shopping. And we don’t even feel manipulated or unsatisfied after purchase. But… Do you know why it’s that effective on purchase decisions? Let’s learn it.
Why Is Psychological Pricing Effective For Your eCommerce Business?
We, humans, are full of emotions, and when it comes to decision-making, emotions play a big role.
When we shop, whether it’s online or in-store, our emotional state can heavily influence what we buy, how much we spend, and even how we perceive the value of a product. For example, excitement, desire, or even stress can drive us to make impulse purchase decisions.
While we like to think that we make choices based purely on logic and facts, the reality is that emotions often guide our actions, sometimes without us even realizing it.
This is particularly true in the context of purchase decisions.
For example:
- If we feel happy or enthusiastic about a product, we’re more likely to see it as worth the price, even if it’s higher than what we originally intended to spend.
- Similarly, feelings of uncertainty or fear can also prompt quick decisions, especially when faced with a “limited-time offer” or low stock availability. This emotional reaction, known as fear of missing out (FOMO), can override our logical desire to shop around or take more time to decide.
And we all have been there and done that.
The reason psychological pricing works effectively is that it considers customers’ emotions, subtly influencing them by playing on human tendencies such as the desire to invest in a good deal, the fear of missing out, and the satisfaction of making the right choice.
So, when you set pricing for your catalog that’s determined psychologically and works exactly to get in line with customer’s emotions, convincing them to purchase will be an easy process.
And ultimately, it will work wonders for your sales numbers.
Next up, we’re discussing some of the best psychological pricing strategies that you should try your luck with.
What Are the Top 12 Psychological Pricing Tactics & Strategies In eCommerce?
Up until now, we’ve understood psychological pricing and how it works to influence purchase decisions.
In this section, we will explore 12 effective psychological pricing tactics and strategies that you can implement in your sales & marketing efforts. Here I’ve listed them.
- Charm Pricing
- Price Anchoring
- Odd-even Pricing
- Decoy Pricing
- Innumeracy
- Price Appearance
- Center Stage Effect
- High-Low Pricing
- Trial Pricing
- Scarcity
- Slash on MSRP
- Flat-rate Pricing
Let’s start by exploring & understanding them.
(& I bet you’ll find them familiar with your shopping experiences until now. 😉)
#1 – Charm Pricing
Charm pricing, also known as odd pricing, is when you set prices at odd numbers falling under round numbers — such as five, seven, or nine — to attract customers looking for a valuable deal.
A study by Dan Ariely, a renowned behavioral economist, found that people were more likely to purchase a product priced at $4.99 than one priced at $5.00, even though the difference is only a penny.
Example of Charm Pricing
Here are some examples of charm pricing:
- Fashion — Clothing items priced at $29.99 instead of $30
- Electronics — Gadgets priced at $499.99 instead of $500
- Groceries — Items priced at $2.99 instead of $3
- Restaurants — Meals priced at $14.95 instead of $5
- Services — Subscriptions & memberships priced at $39.99 instead of $40
How Does Charm Pricing Influence Customer Behavior?
This psychological pricing strategy helps as our brains are wired to seek out deals and discounts that seem cheaper.
See, usually, customers read from left to right with attention span decreasing very steeply. And when charm pricing is in action, your customers might interpret the $4.99 pricing format as $4 rather than $5, making the price seem lower.
This might sound manipulative, but still, humans are indeed pain-avoiders.
So, when you (as a seller) charge in a format of $4.99 instead of $5 as an entire, your customers will think of it as a bargain price. But again, you know it’s a psychological strategy to charm your customers. 😉
#2 – Price Anchoring
Price Anchoring is another psychological pricing tactic where the initial pricing is set as higher compared to the one coming after it. This strategy is based on the human tendency to rely heavily on initial pricing information.
So, when the first price (the anchor) is set as high, the latter ones seem less expensive in comparison.
This pricing strategy has a simple goal to draw attention toward a product/service at low–cost. And is common for both product-based or saas based companies.
Example of Price Anchoring

Here’s an example of price anchoring.
Imagine you’re shopping for a laptop. You first see a high-end model priced at $2,500. This becomes your anchor price.
Now, when you see another laptop priced at $1,900, it seems like a much more reasonable deal compared to the initial $2,500 anchor.
Apart from that, I recently went shopping and noticed how strategically the prices were set. After seeing 1st price boards with a higher price mention, the other price boards seemed more affordable.
This definitely influenced me to visit those sections with added interest.

Something similar must’ve happened with you as well, be it while shopping in-store, online, or when purchasing any subscription plan.
How Does Price Anchoring Influence Customer Behavior?
We humans tend to compare. Shopping decisions are made only after comparing products and their prices.
When customers are presented with a high price at first (the anchor), it becomes a benchmark against which they compare subsequent prices. This creates a psychological effect known as “relative perception”. This relativity can help influence customer’s purchase decisions.
If a customer is seeking budget-friendly options and is initially presented with a high anchor price (which is beyond their budget), subsequent prices may appear more affordable in comparison. This is because they have already seen a more expensive option, so the lower-priced alternatives seem like better deals.
This can lead them to settle with its pricing as it seems reasonable and valuable compared to the anchor.
Another thing, when implementing this psychological strategy, your target product is not the product with the anchor price, but rather the subsequent products that benefit from the comparison.
#3 – Odd-Even Pricing
Odd-even pricing is a psychological marketing technique where a business sets a price to end in an odd or even number (such as $0.99 or $1.00) to influence how customers perceive the product’s value.
What is Odd Pricing?
The Odd-even pricing strategy is similar to charm pricing, yet it is different and applied on a broader scale.
This strategy is based on the belief that psychologically, buyers are more sensitive to certain ending digits, particularly odd numbers like 1, 3, 5, 7, and 9. For example, a t-shirt is priced at $9.93.
What is Even Pricing?
Even pricing, on the other hand, is the exact opposite of odd pricing. Here, the pricing numbers end with 0, such as $10. The goal of even pricing is to convey a sense of accuracy, maintain simplicity, and present the product as high-quality, often positioning it as a premium offering.
It’s necessary to consider that this pricing strategy is used for different niches and sales channels to bring in better results.
Example of Odd-Even Pricing
Here are the examples of Odd Pricing:
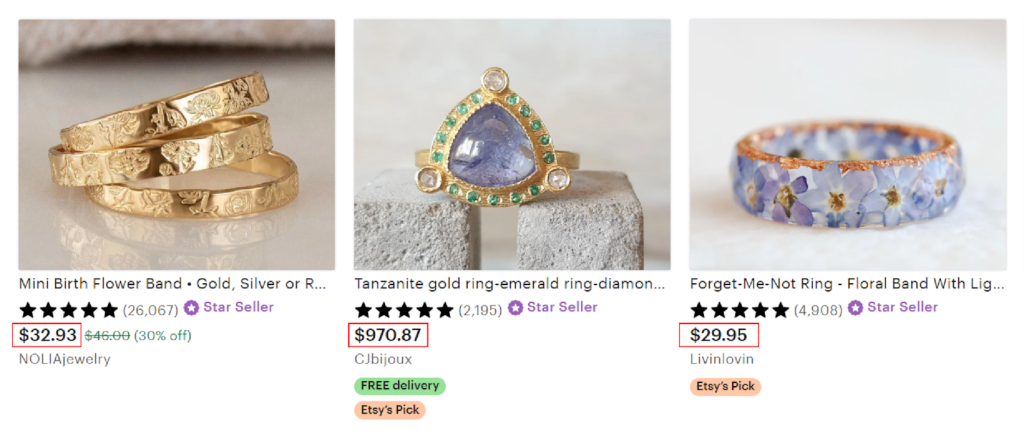
- Fashion — Clothing items priced at $25.95
- Electronics — Gadgets priced at $499.99
- Groceries — Items priced at $2.75
- Restaurants — Meals priced at $14.97
- Services — Subscriptions & memberships priced at $78.35
Here are the examples of Even Pricing:
- Luxury watch priced at $1,000.
- Spa services are offered at $200.
- Fine dining restaurants charge $100 for a set menu
How Odd-Even Pricing Influences Customer Behavior
Both of these pricing strategies convince customers differently yet effortlessly. Let’s check how.
How Odd Pricing Works
Just as we discussed earlier our brains tend to focus on the first digit of the price, when we are faced with a t-shirt costing $4.57 we only focus on the first digit, which is $4, and not for 75 cents coming along. This creates an initial impression of the price being in the $4 range. The subsequent digits, 75, are often processed less consciously.
So, when your customer, at first, sees a lower price, positive emotions and a sense of satisfaction are triggered, making them more likely to purchase that product.
How Even Pricing Works
While Customers prefer a 99-ending for low-priced items over a cheaper 95-ending, this expectation changes for high-priced items.
For example, a pizza priced at $4.95 will generate higher sales than if it were advertised at $5.00.
However, if a food processor is priced at $59.99, the sales volume will be lower than if it were advertised at $60.00, a standard price. In this case, a 99-pricing format would damage the customer’s perception of product quality.
When shopping online, you’re more likely to find the application of the odd-even pricing strategy (like $6.73 instead of $7 and $400 instead of $399).
For once, charm pricing (e.g.: charging $4.99 instead of $5) might not work out its charm, as people tend to think more rationally and reconsider their purchase decisions. However, the odd-even pricing strategy often works best when used right way
#4 – Decoy Pricing
Decoy pricing is a psychological pricing strategy that uses a third option, called the decoy, to make another option appear more appealing. With this pricing strategy, the goal is to influence customers into choosing the more expensive and profitable option.
In easy words, decoy pricing is about introducing an undesirable option to push customers towards a higher-priced option.
Example of Decoy Pricing
Here’s an example of Decoy Pricing from Apple.
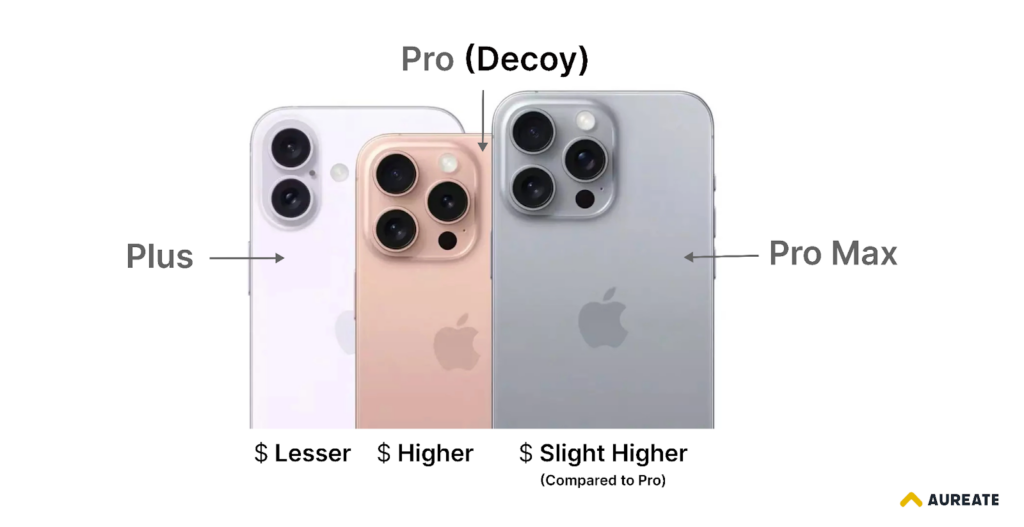

Apple’s pricing strategy for its iPhone models is a prime example of decoy pricing.
First of all, the company offers several options, including the Plus, Pro, and Pro Max versions.
While the Pro Max is slightly more expensive, the price difference is often minimal when compared to its Pro versions. This subtle difference in pricing makes the Pro Max model seem like a more attractive value, encouraging Customers to choose it over the base model. By creating the perception of getting more by spending some extra bucks, Apple effectively influences consumer purchasing decisions.
How Decoy Pricing Influences Customer Behavior
Customers are easily attracted when presented with choices.
Whether it’s deciding on a Netflix subscription or picking a popcorn size, we often try to choose the best option out of three. It’s the moment we bring out our inner genius to make the best possible choice, right? 😉
Let’s take popcorn tub sizes as an example. They come in three sizes: small, medium, and large.
Here, we tend to care the least about the small size since it already appears to offer less value compared to the medium and large sizes.
Now, when you’re deciding between the medium and large (which has an added benefit), your mind naturally gravitates towards the large size. This happens because the price difference between the two is often small.
So, we think the large size is the better deal, even though the medium one is just overpriced.
This is a classic case of FOMO on a good deal, influencing customers to choose the option that seems to offer better value based on this comparison.
#5 – Innumeracy
Innumeracy is a psychological pricing tactic that takes advantage of people’s difficulty in differentiating between certain price points. This strategy takes advantage of customers’ inability to perform basic mathematical calculations, which leads them to make irrational purchase decisions.
This is a very common technique to help you show your prices as more appealing to customers.
Example of Innumeracy
- Using uneven numbers to set pricing (such as $78.89 instead of $80)
- A store showing a “50% off” offer as “buy one get one free”.
How Innumeracy Influences Customer Behavior
Innumeracy, or the human tendency to not care about calculating prices when shopping helps in selling more.
Yes, there are multiple ways businesses take advantage of that.
Normally, when customers are presented with complicated pricing, discounts, or deals, they get confused. For example:
- When we see products priced at $78.89 or $24.86, our brain will fetch the price to be $78 and $24 without considering adding cents that we gotta pay, showing the price to be bargained. Hence, better selling for stores.
- When a store offers a “Buy 1, Get 1 Free” offer, we get excited and think of purchasing without calculating whether it’s a good deal or not. All we saw was the word “FREE”, which made us jump right into purchasing, even when we could get better options somewhere else.
This is because customers think less rationally and more emotionally when dealing with any offers.
As a result, it works out well for store owners to influence purchase choices.
#6 – Price Appearance
Price appearance is another psychological pricing strategy that refers to how price appearance can impact a buyer’s psyche, leading them to take an interest in the product.
Example of Price Appearance

- Minimalist Display Of Pricing — A store is selling shoes for $100, but instead of showing the price as “$100.00,” they list it as “$100” or $99.99”.
- Discounted Pricing — A product was originally priced at “$50,” but the store lists it as “Now $49.95” instead of “$50”.
- Without Comma — A product that costs $1,499 might be shown as “$1499”.
How Price Appearance Influences Customer Behavior
A slight change in how you place a price can make a big difference in how your customer perceives it.
We, humans, easily get tricked.
Yes, when a price that’s smaller, more subtle, or placed in a less noticeable spot, we focus on the product more than the cost. So, in the end, we consider pricing to be subtle and genuine.
And on the slip side, if the price is bold and is placed long which pops right into your eye, you may find it to be expensive. For example: $4,555.00 seems like a huge amount compared to $4555 until we take in our rational thoughts.
#7 – Center Stage Effect
The center stage effect is a psychological pricing strategy that involves positioning a product/service in the center of a group of similar products to make it appear more appealing to customers. This is based on the human tendency to pay more attention to items that are located in the center of their visual field.
In easy terms, the center stage effect is about placing a target product or service in the middle of options that guide customers to choose it.
Example of Center Stage Effect
Some of the examples of the center stage effect include:
- Grocery Store — Placing a popular product in the middle of a display case.
- eCommerce — Featuring a featured product on the front page of a website.
- Subscription — Adjusting pricing structures that show middle-tier options as more appealing.

How Center Stage Pricing Influences Customer Behavior
The center stage effect is when your standard tier plan is presented in the middle in a way that makes it appear to be the best balance of cost and value—with some added features but at a discounted price.
Customers, as usual, tend to pay more attention to items located in the center of the visual field.
Also, it’s psychologically believed that when a customer checks for a subscription plan, their attention is drawn to the center as a human brain naturally finds the first plan to be cheaper and the last one to be most costly.
Finding a middle ground is the entire motive for seeking the best balance in a deal.
When you position your offerings in the center, which customers seem to glare at most, convincing them will be an easier task.
#8 – High-Low Pricing
High-low pricing is a pricing strategy where retailers set high prices for products and then offer frequent discounts or offers.
In exact, with this pricing strategy, retailers (at first) set prices above the perceived market value of the product. And later during checkout, or some seasonal flash sales, discounts are offered to interested customers in purchasing.
This creates a perception of value and can attract customers who are looking for bargains.
Examples of High-Low Pricing

- Department stores — Regularly offering sales on clothing, electronics, and home goods.
- Grocery stores — Using weekly ad circulars to advertise discounted prices on specific items.
- Online retailers — Running flash sales or limited-time offers on a variety of products.
How High-Low Pricing Influences Customer Behavior
With this pricing strategy, customers are initially presented with higher prices, which they perceive as a benchmark or an expensive item. At this point, their brain has considered that high-value product to be luxurious and exclusive.
Later, when a customer finds that this product has a discount—be it during checkout or in upcoming sale seasons—they anticipate grabbing it as a quick deal, without giving a second thought to purchasing.
When implemented effectively, this strategy can help increase sales, encourage repeat purchases, attract more customers, and boost sales of complementary products.
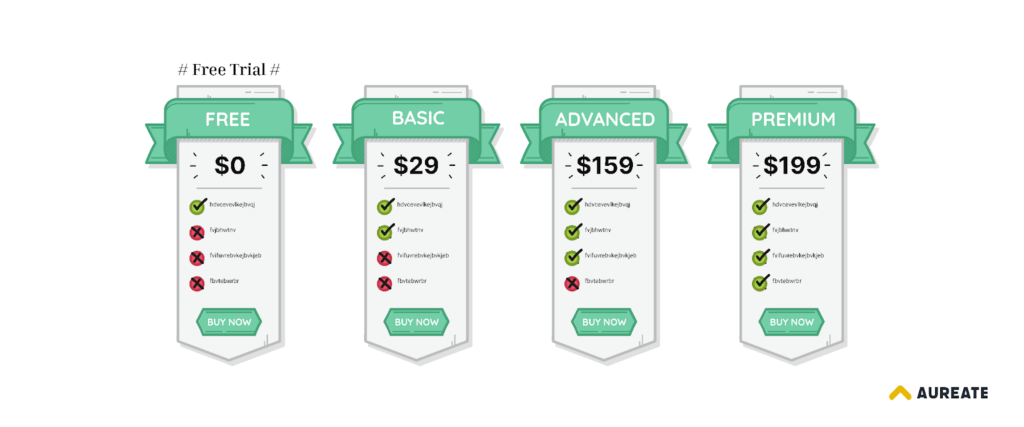
#9 – Trial Pricing
Trial pricing is another psychological sales tactic where a product or service is offered at a reduced price or for free for a limited period of time.
This sale strategy helps customers to try out a product or service before committing to its full price.
A trial period for any service might last for a few days, weeks, or months. If you want to apply this pricing strategy to your products, packaging them in small quantities is recommended. Later, you can either offer them to your customers as gifts with their purchases or allow them to buy at a reduced price.
Example of Trial Pricing
- Free samples — Offering small samples of food, cosmetics, or cleaning products.
- Introductory offers — Providing a discounted price for a first-time purchase.
- Free trials — Offering a limited-time trial of software applications or online services.
- Freemium models — Offering a basic version of a product or service for free, with premium features available for purchase.
- Free trial periods — Offering a free trial of a subscription service, such as a streaming platform or a fitness app.
- Test drives — Allowing potential car buyers to test drive a vehicle before making a purchase.
How Trial Pricing Influences Customer Behavior
Customers have a list of doubts before they finally hit the Buy Now button, such as:
- Will this product or service work for my requirements?
- Does the quality justify the price?
… and more such questions that drive them away from purchasing from you.
& It’s a fact — be it for services or products.
When you (as a business) allow them to take a trial, evaluate your product/service, and try to answer their concerns without asking to invest in full-price, it helps you evoke positive emotions in customers.
When customers see trial options, many are willing to pay a small amount to try it out.
So, what leads customers to invest in full price are trial packs, as they only ask for a small amount or come for free.
As a result, you’ll be able to pull a lot of your target audience into trying your products, and after trial, if it works with their requirements, they’ll easily make a purchase. Hence, your journey to convince them becomes easy.
#10 – Scarcity
Scarcity is a psychological pricing strategy that uses limited availability or exclusivity to increase demand for a product or service.
It’s based on the human tendency to value rare items more, which leads customers to buy instantly.
Examples of Scarcity Pricing
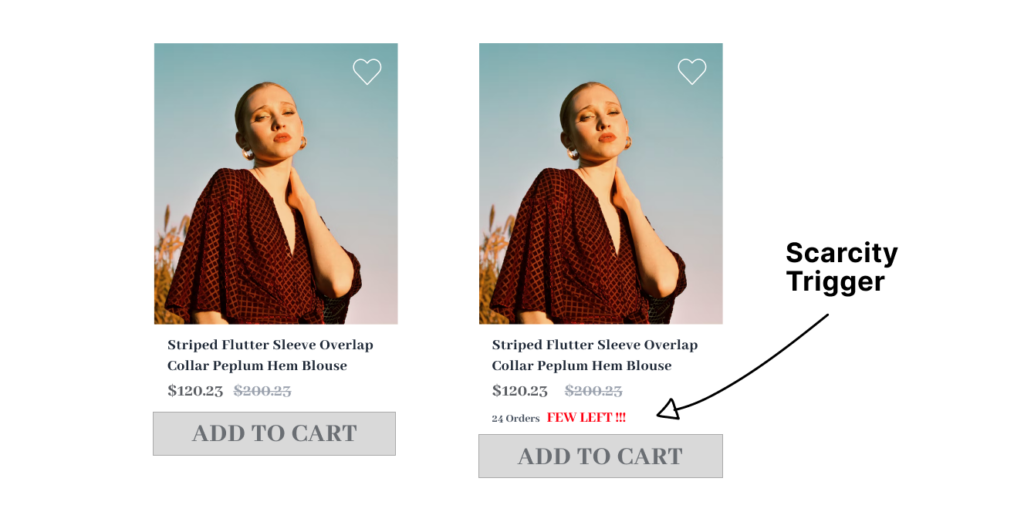
- Flash sales — Offering a steep discount on a product or service for a short period.
- Seasonal promotions — Limiting the availability of products or services to specific seasons or holidays.
How Scarcity Influences Customer Behavior
Customers believe, if something is running out of stock or some pricing is short-lived, it’s worth purchasing.
Thus, raising the appeal of the product.
This is because scarcity triggers a psychological reaction known as fear of missing out (FOMO).
FOMO brings in the idea of missing out on something valuable, which (in turn) pushes customers to take action and avoid losing the opportunity to buy it.
So, when you show that your product is selling out quickly, your customers will see it as a sign to buy it as soon as possible, because in their eyes, other people have already grabbed the deal, making it seem valuable.
That’s how scarcity makes your customers chase after your product.
Also, this strategy helps increase post-purchase satisfaction. Yes, when customers own something that’s hard to get & achieve, they find it special, exclusive, and rewarding.
#11 – Slash the MSRP
Slash the MSRP is a common psychological pricing strategy that involves prominently displaying the original, often inflated, Manufacturer’s Suggested Retail Price (MSRP) alongside the discounted selling price.
This strategy pins the human tendency to focus on savings, thereby convincing customers to purchase the product.
Example of Slash the MSRP
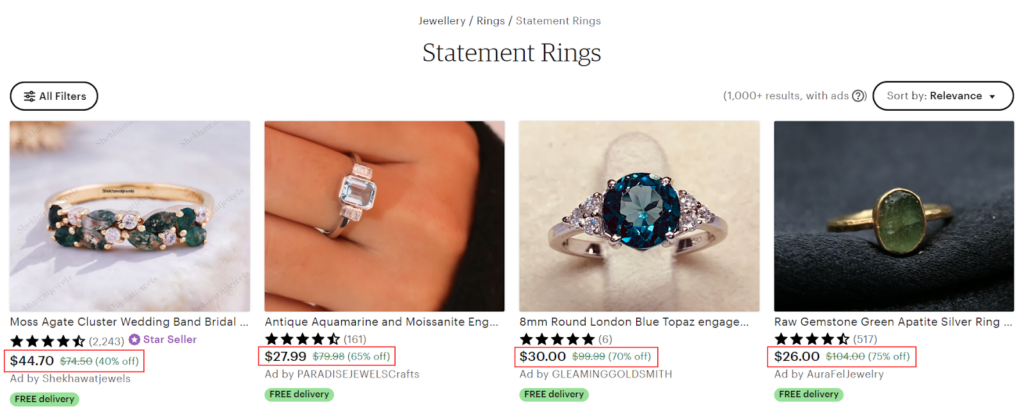
How Slash on MSRP Influences Customer Behavior
Many businesses choose to sell right at MSRP, however, most of the businesses know a secret so they simply strike through the MSRP and sell the item for a lower price. Why is that?
They can simply sell at a lower price without striking the MSRP.
Well, that’s a widely-used strategy.
Psychology says that when customers see a slash on MSRP, offering a better deal on a product, they consider the MSRP as an anchor to which they compare the offer price, which is lower.
So, with that, customers feel like they can actually save money by purchasing that item.
#12 – Flat-rate Pricing
Flat-rate pricing is a pricing model where a business or individual charges a fixed fee for a product or service, regardless of the time, materials, or factors involved. Flat-rate pricing is also known as “fixed fee” or “flat fee” pricing.
It’s used in various business niches, including software, shipping, home services, grocery, and more.
Even some fashion & beauty stores follow this pricing strategy to show their products as exclusive and to simplify buying decisions.
Example of Flat-rate Pricing

- Subscription services — A monthly or annual fee is charged for access to a product or service, such as a tool subscription.
- Food Stores — Selling burger for $1.5
How Flat-rate Pricing Influences Customer Behavior
Flat-rate pricing takes a totally diverted route on convincing customers.
First off, it makes things super straightforward. Yes, no customer likes the confusion of hidden fees or complicated costs, right? With flat-rate pricing, customers know exactly what they’re getting into, giving them the comfort to make purchase decisions without comparing prices or figuring out what they’ll really pay.
With a single stated price that’s non-negotiable, customers can decide faster, reducing the chance they’ll bail on their purchase.
But what about the human tendency to seek better deals and discounts?
Well, that matters for sure. However, for multiple things, when customers are presented with a flat price that’s non-negotiable, they think it’s the right and valuable price only, as it’s consistent from and for forever.
Also, when the product is used often, they will trust flat prices only.
Like, do we want the price of Coke Can or Noodle Pack to fluctuate each season? Definitely not!
;
That’s all about the top 12 psychological pricing strategies
Advantages & Disadvantages of Psychological Pricing
In this section, we will explore the key advantages and disadvantages of psychological pricing, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of its potential benefits and drawbacks.

# Advantages of Psychological Pricing
Here, I’ve listed the potential advantages of psychological pricing strategies that we discussed above.
1. Attracts More Attention
Psychological pricing draws people in by instantly making the deal feel more appealing.
Take “$9.99” vs. “$10” pricing as an example—even though the difference is only one cent, the $9.99 price grabs better attention compared to the round figure pricing. This is because our brains focus on that first number more.
So, when your customer sees a “9” instead of a “10”, we find a product to be cheaper.
This grabs customers’ attention, making them pause and consider the offer instead of scrolling past it.
2. Provides Better Experience to Buyer
Using psychological pricing makes the whole shopping experience smoother and less stressful.
When prices are displayed more logically and in a clean, simple way—like using smaller fonts or subtle formats—customers feel less overwhelmed.
It becomes easier for them to digest the costs coming with it, and they even get that little thrill of “saving” which adds a fun element to the shopping process.
Instead, when customers are bombarded by big, scary price tags, they might feel anxious and run away.
3. Is Inexpensive and Easy
Psychological pricing is a no-brainer as it’s easy and cheap to implement.
When you choose to implement the strategies, there’s no need to run huge discounts or spend money on fancy campaigns—all you need to do is understand your customers and make changes to your prices in a way that works right for their psyche.
You can drop a few cents, remove a comma, or even just make the price look smaller, and it works.
Despite requiring minimal effort, these strategies contribute greatly to improving conversions.
4. Helps Reduce Price Sensitivity
Psychological pricing can make your customers focus less on actual cost and more on the perceived value.
When prices are designed to feel lower (like $98.89 instead of $100), customers don’t feel as picky or sensitive about the price. They stop nitpicking over small differences and focus more on the benefits of the product.
This helps you sell products at prices that might’ve seemed too high if presented normally, making your customers more willing to spend without overthinking it.
5. Increases Overall Sales
Earlier, we saw that psychological pricing helps attract customers, provides a better buying experience, and helps reduce price sensitivity. This will have an overall effect on your sales numbers.
Yes, when customers are less likely to hesitate or second-guess the price, they’re more likely to purchase it.
# Disadvantages of Psychological Pricing
Here, I’ve listed the potential drawbacks of psychological pricing strategies that we discussed above.
1. Won’t Work Always
Many customers think rationally when shopping.
So psychological pricing strategies that work for one product or audience might totally flop for another. Also, most customers can see through your strategies and won’t be swayed by tactics of using “$9.99” instead of “$10”.
But, there’s always a scope when you use some brainer and make things work in your favor.
2. Can Appear Manipulative To Customers
Let’s be real—don’t we all recognize some of the strategies brands use on us?
Your customers might as well catch on and think that they’re being manipulated by constant pricing tricks, which could damage your brand image in their eyes. After all, every customer is aware of being played.
To avoid such scenarios, conduct thorough research and make well-thought-out decisions.
;
That’s all for the benefits and drawbacks of using psychological strategies.
Well, to avoid the disadvantages, I’ve added some tips for you to follow, in the next section. Scroll up a little.
Psychological Pricing Best Practices
Here, I’ve listed some best practices that people use to get better results from setting psychological pricing strategies. Let’s check.
1. Price Smart, Not Random
Making tweaks to pricing doesn’t mean using random numbers.
You need to choose pricing numbers strategically, and they should have a purpose.
Every price point must align with your product and the value it offers. When you set prices thoughtfully, it ensures you’re attracting the right customers and hitting that sweet spot where they feel like they’re getting a good deal, without undervaluing your product.
2. Don’t Overdo
While psychological pricing strategies are effective, going overboard can backfire as well.
For example, constantly slashing prices or using too many pricing tricks at the same time can make your brand seem gimmicky or even shady, leading customers to feel like they’re being manipulated.
So, it’s important to use these strategies with ease.
All you need to do is keep things real and straightforward to avoid overwhelming customers.
3. Always Be Optimizing
Market trends and customer behavior keep changing over time.
So, the pricing strategy that is working today, might not work that well in the future. Make sure to keep optimizing based on customer behavior and reactions to it. This will help you stay competitive and ensure you’re always optimizing for more sales.
Just that, don’t use the “set it and forget it” approach here.
When The Psychological Pricing Strategies Won’t Work?
If you sell luxury products, most of these pricing strategies won’t work for you.
- Will a Gucci customer care if the price is set at $975.89 instead of $1000.00? — They won’t.
This is because, when you sell luxury products, you want people to value your product, not the price.
Also, the target audience of luxury products won’t care about grabbing onto cheap deals as their focus is centered on the product and its quality.
So, in most cases, your efforts of psychological pricing may go to waste, if applied to luxury products.
LAST WORDS
In this article, we learned that psychological pricing is a way to get inside your customer’s heads and nudge them towards purchasing, without them even realizing it. We also understood 12 strategies to help you get ahead, along with considering areas to make it work well.
I hope this article provided enough information on how you can implement those strategies.
Now is your time to understand and implement the right strategies for your product catalog.
Contact Us if you need further guidance.






Post a Comment
Got a question? Have a feedback? Please feel free to leave your ideas, opinions, and questions in the comments section of our post! ❤️