In this series of building eCommerce websites from scratch, the article will cover everything about product page optimization that experts are hiding from you. We discussed the must-have eCommerce website pages list in the last chapter. But that’s not enough. It’s important you optimise these pages for better results. I have tried to craft the steps I use to optimize any product page.
I want you to read all these steps carefully and try implementing them on some of your product pages initially. They’re simple. Don’t take much time. Plus!! You can take charge of your store.
Before I begin, here’s a fair warning. Most of these product page tips have worked for me at large. But some of these didn’t want me happy.
But you can implement all the tips and measure their impact on your eCommerce business. In case you’re worried about how to measure them… I will also cover the measuring techniques for you. So, shall we get started?
- Tip #1: Start With A Serious Keyword Research
- Tip #2: Optimize Title Tags
- Tip #3: Add Product-Related FAQs
- Tip #4: Write Unique Product Details
- Tip #5: Include Product Reviews & Get Social Proof
- Tip #6: Optimize All Media Types
- Tip #7: Speed Up Product Pages
- Tip #8: Focus On Product Availability
- Tip #9: Avoid Manufacturer’s Product Descriptions
- Tip #10: Audit Technical Issues On Your Product Pages
- Tip #11: Use MarkUp Schema On Product Pages
- Tip #12: Test The Product Pages
- How To Measure The Impact Of Product Page Optimization?
- Conclusion
- Frequently asked questions
Tip #1: Start With A Serious Keyword Research
While researching the product page keyword, I like maintaining a small excel sheet with the list of competitors’ SEO titles, meta descriptions, and headings.
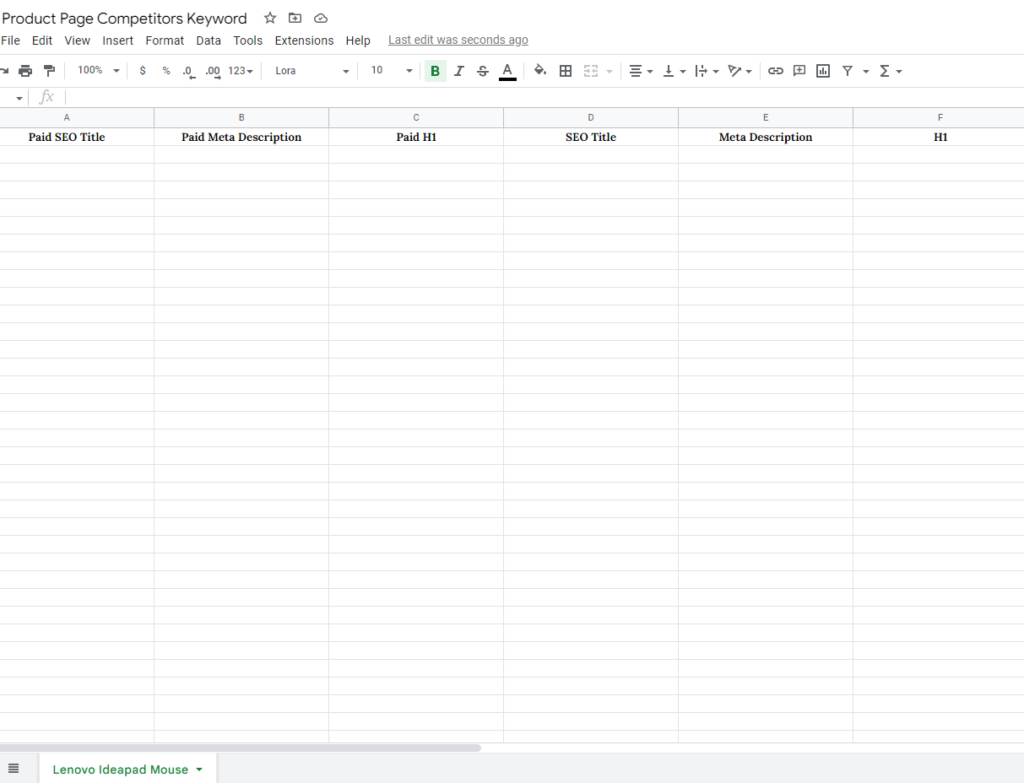
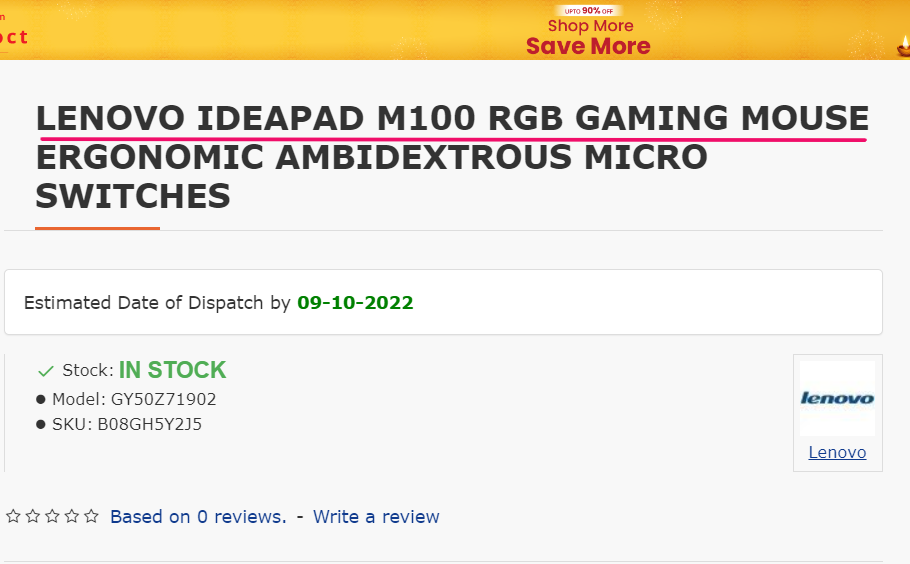
The idea is to track all the commonalities in the product name. For example, if you sell a “Lenovo Ideapad Mouse,” you’d like to begin by noting down what your competitors have written.
Here’s how you can populate the sheet.
Step 1: Install the free VPN for the non-manipulated search.
I use the Hoxx VPN proxy to select the country I want to target. You can choose any free VPN for it. Once you’ve installed it in the browser, you’re good to make a non-manipulated Google search.
Step 2: Download the SEO Extension.
Then I use SEO extensions like SEO Pro or SEO minion to capture SEO details. You will find the SEO details in one place for the particular product page.
Step 3: Google search your product.
Search your product on search engines. For simplicity and accuracy, let’s keep it a Google search.
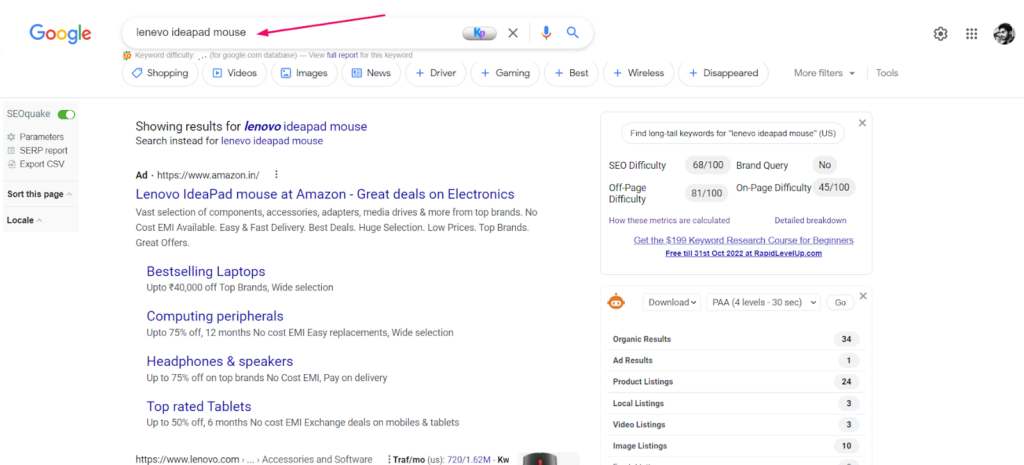
Step 4: Note down all the paid & organic results from SERP
Open all the paid, organic, and shopping search results.
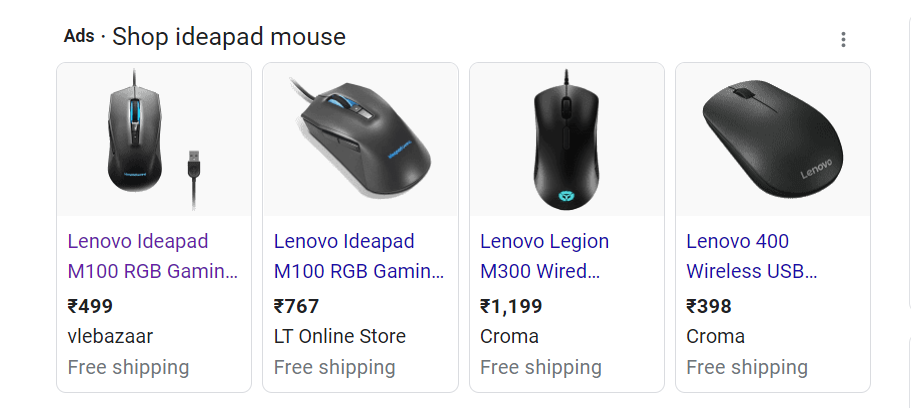
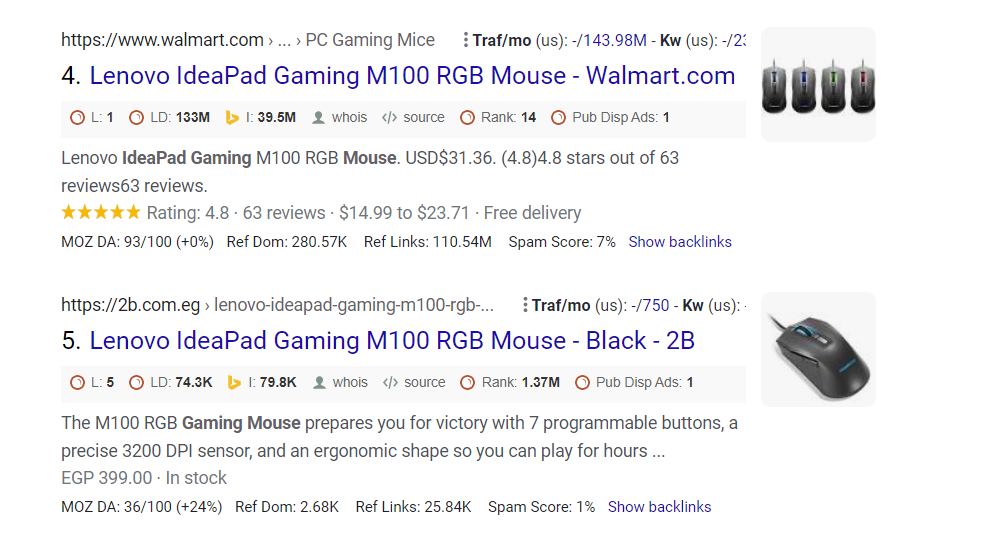
Step 5: Run the SEO tool
Run the SEO tools on the competitor’s product page and copy the list of titles, descriptions, and heading in the table.
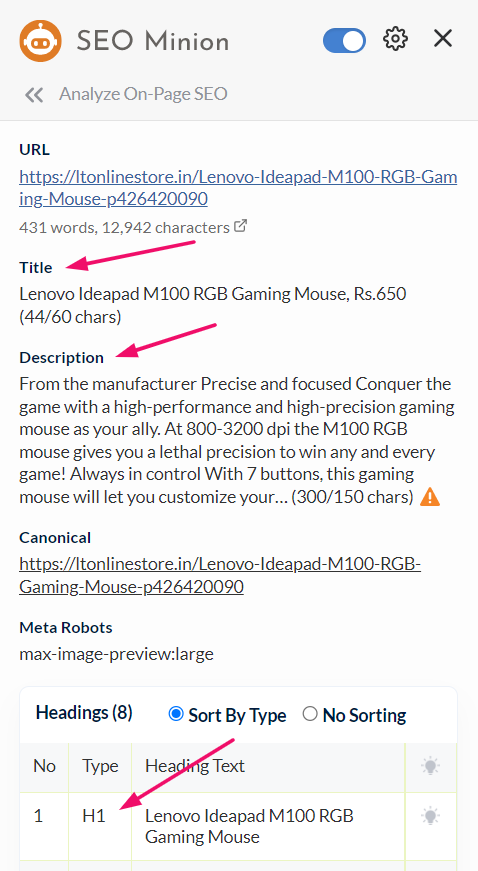
Step 6: Find the commonalities in the table
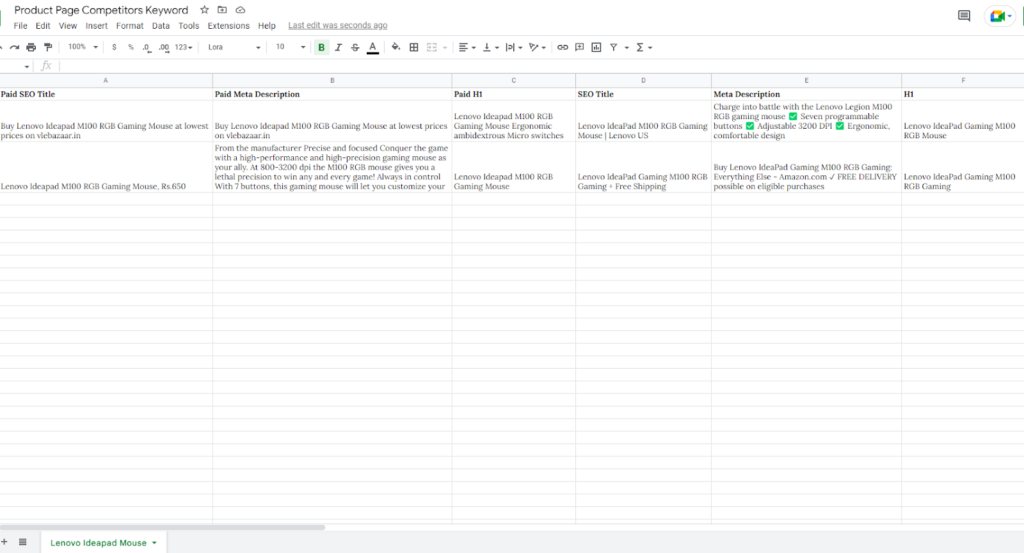
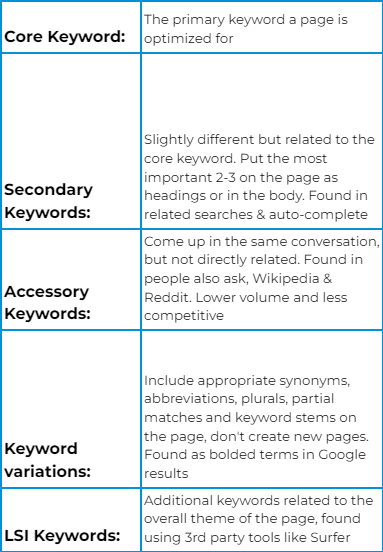
As you can see, most competitors use the “Lenovo IdeaPad M100 RGB Gaming Mouse” keyword in their title tags. So it is a decent keyword to start with.
Step 7: Bonus Step
The steps are tiring. So I take the help of Google’s rich comparison snippet.
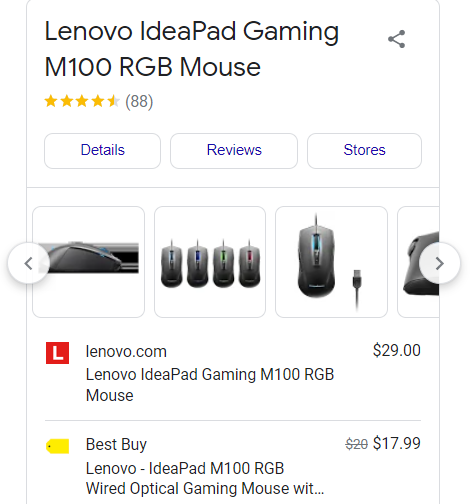
The rich snippet has a comparison feature. You not only get the product title details. But also the price and deals.
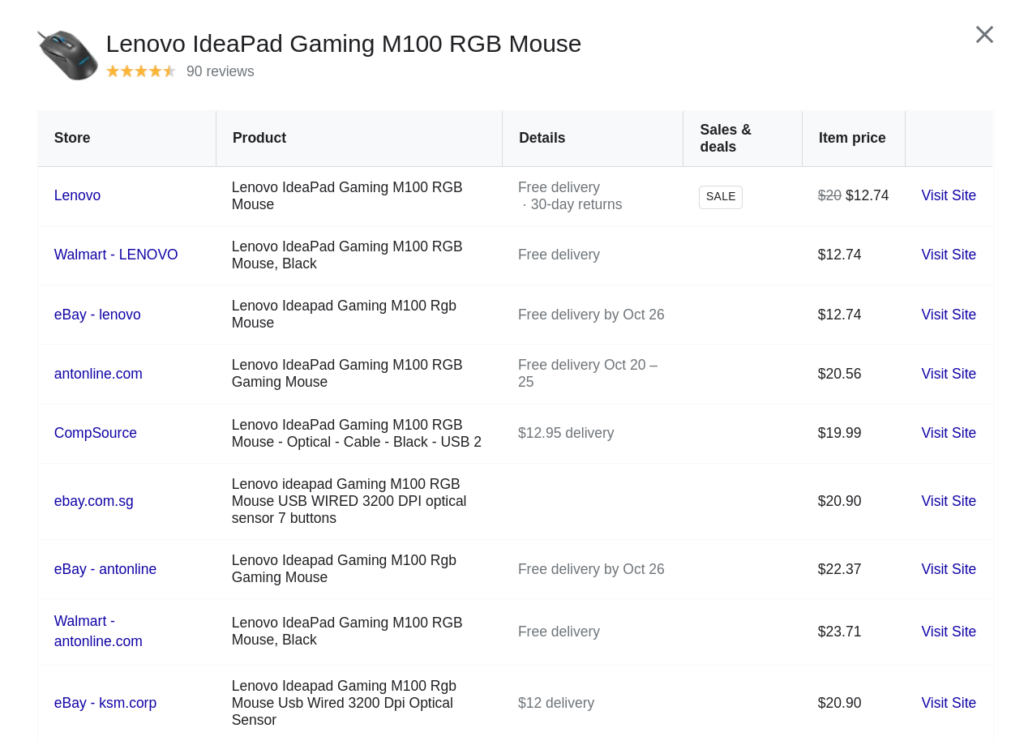
This was just one of the ways to research keywords for the product pages without using any tool. There are many other tool-based approaches, but let’s keep it for another day.
Important note
- If you run a product query on Google and a paid ad shows up, it’s certainly the keyword you want to go with. It already has a transactional intent, so the chances of conversion rate are high.
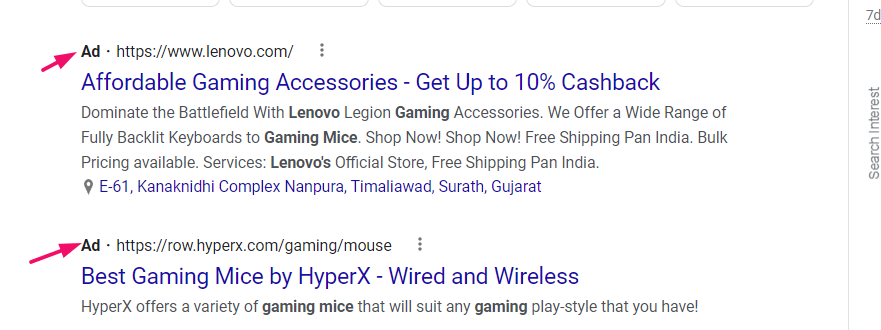
- You also want to list the product page’s secondary, accessory, and related keywords. The primary keyword is not enough, as you want to optimize your product pages for keyword variations.
Tip #2: Optimize Title Tags
Another advantage of listing the competitors’ title tags in the excel sheet is benchmarking their data and repurposing them for your online store.
Step 1: Title Optimization
Let’s say you wanted to write the product’s SEO title. You can check the commonalities and differences. Below you can find the underlined commonalities and differences in the box.
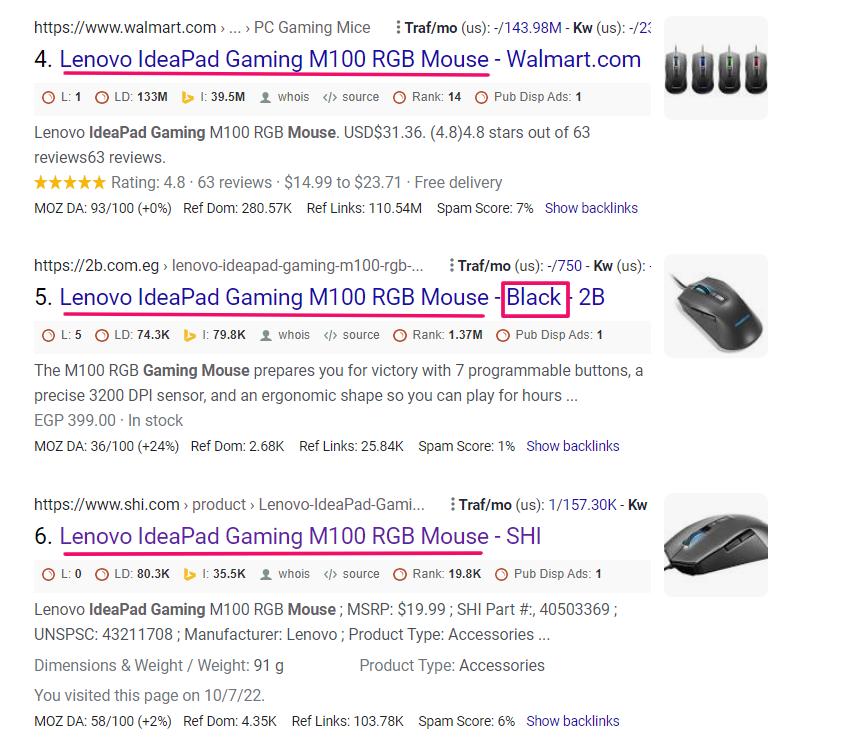
You have to take care of two things:
- Use what’s common in all the titles
- Write your USP (Anything instead of black in this case)
Apart from what you write, the length of the title is also a concern. Google re-writes about 61% of the titles. So, in that case, you have to be a little aware of the titles businesses use and the title Google displays. I again manage an excel sheet to track the titles and find out some patterns from it.
For example, Google replaced Amazon’s free shipping title with branded search.
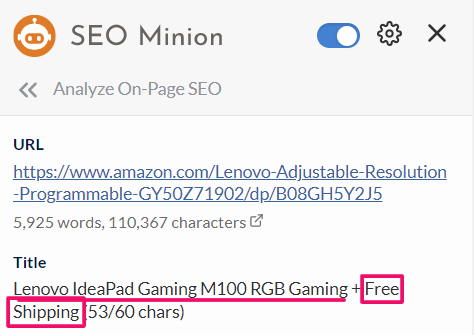
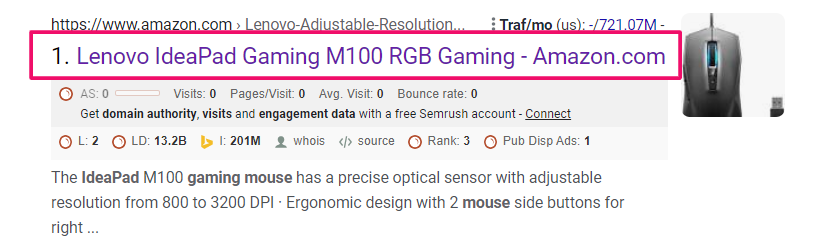
Similarly, note down the title results for all the sellers and populate the excel sheet at least for the first 20 results.
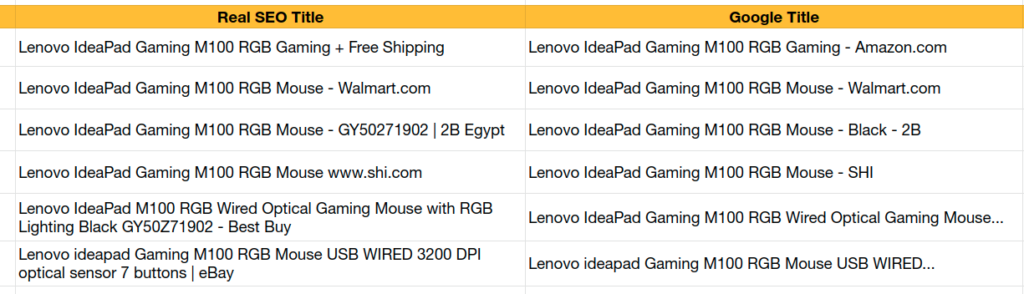
If you observe the table, you’ll realize Google is
- replacing “|” with “-“
- not reading the model number “GY50Z71902.”
- using branded terms at the end of the keyword
So, in this case, you shouldn’t waste pixels writing model numbers, pipes, & lengthy domain names. Just the keyword, small USP, & brand name are enough. Use free tools like ToTheWeb to keep the title pixel length in check.
Step 2: Meta Description Optimization
You can follow the same optimization principle- what you have (correlational data) + what you can offer to optimize your product.
- I pick all the bolded terms in meta descriptions from competitors. They’re nothing but keyword variations.
- Then I spread them evenly.
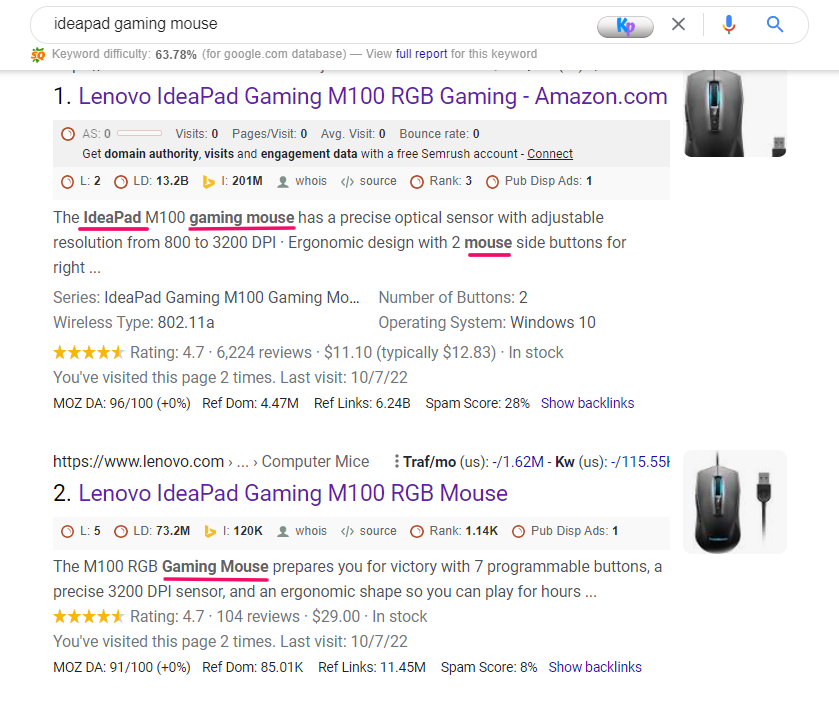
- Next, you can pick up the common terms like free shipping, refund, etc., to make your description passable to Google’s algorithm.
What I have observed with meta descriptions is that Google is less likely to change meta descriptions if you paste 2-3 lines from your body content in the meta area.
For example, Google replaces Amazon’s meta description with the about this item description paragraph.
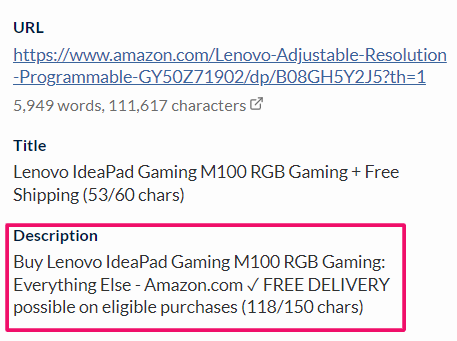
Here’s the proof. So if you can create a sheet for real meta and Google meta, you can observe the pattern of how and why Google is changing the meta. You have the answer if Google picks 7 out of 10 descriptions from the first paragraph.

Finally, you can again use tools like ToTheWeb to keep an eye on meta description size.
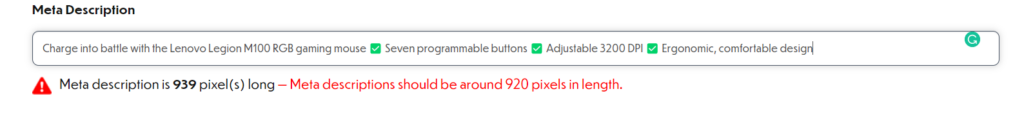
Step 3: Heading Optimization
I have tried it all on the eCommerce store.
- different SEO titles and headings,
- their partial matches, and in many cases,
- the same SEO titles & headings.
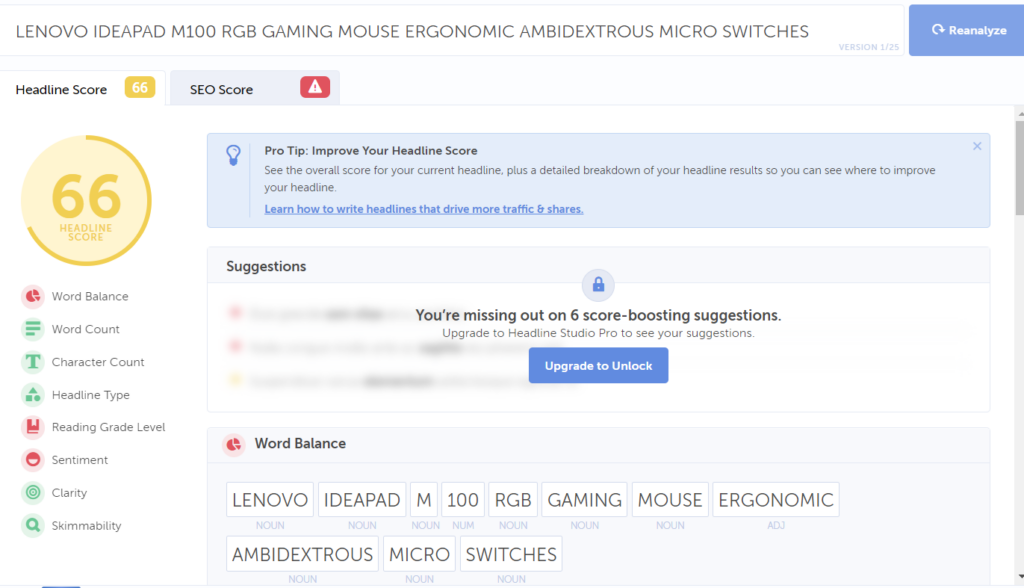
The ones that got me the best results are using the same SEO title and heading. Again, I am not saying it has to be this way. But my experiences and experiments have given me the best results when I keep the SEO title and heading the same. Other things you can take care of:
- Front-load your keyword
- Check your headline score in tools like CoSchedule
Tip #3: Add Product-Related FAQs
Well, this is my favorite section. FAQs are one of the simplest yet most effective techniques for optimizing your product page.
The idea of FAQs is to answer all the long tail queries. I categorize them into two types:
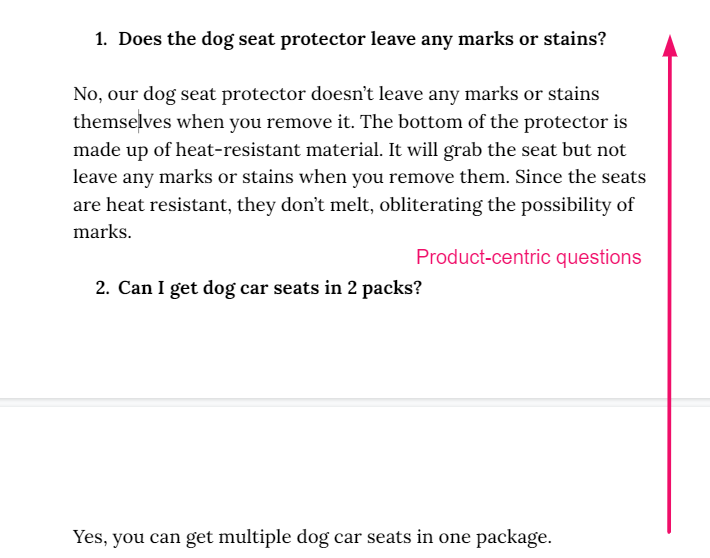
- All the product-centric questions (hyper-relevant questions related to the item you’re selling)
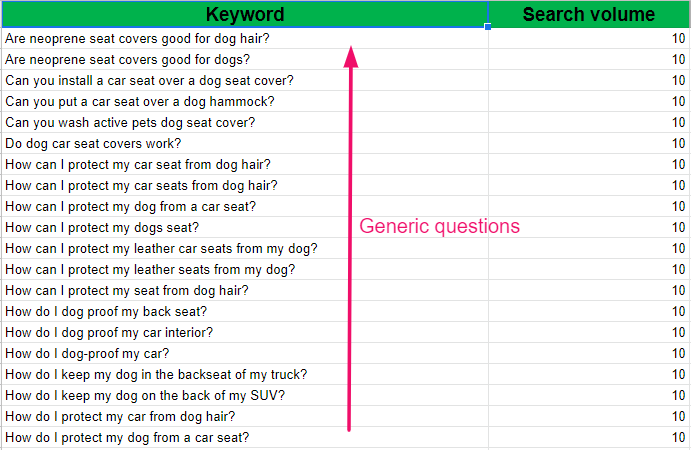
- All the generic questions about the product
Now the bigger question is, where do I get these questions from?
Step 1: Extracting product-centric questions
One way to extract product-related questions is by not extracting them at all. No one knows your product better than you. Ask all the questions that visitors may have. Put them in the sheet. And answer them keeping user experience in mind
For example, if you’re selling a dog car seat cover, users may have genuine questions such as
- What’s the size of the cover?
- Will the cover fit any car model?
- How to wash the cover?
- How to install the cover?
Did you see it? You may not find any of these questions on any SEO tool. But it’s important to answer them because they talk about your product. If you can’t think of many questions, here’s a little hack you can apply.
Go to Amazon >> Search the product >> Customer questions & answers
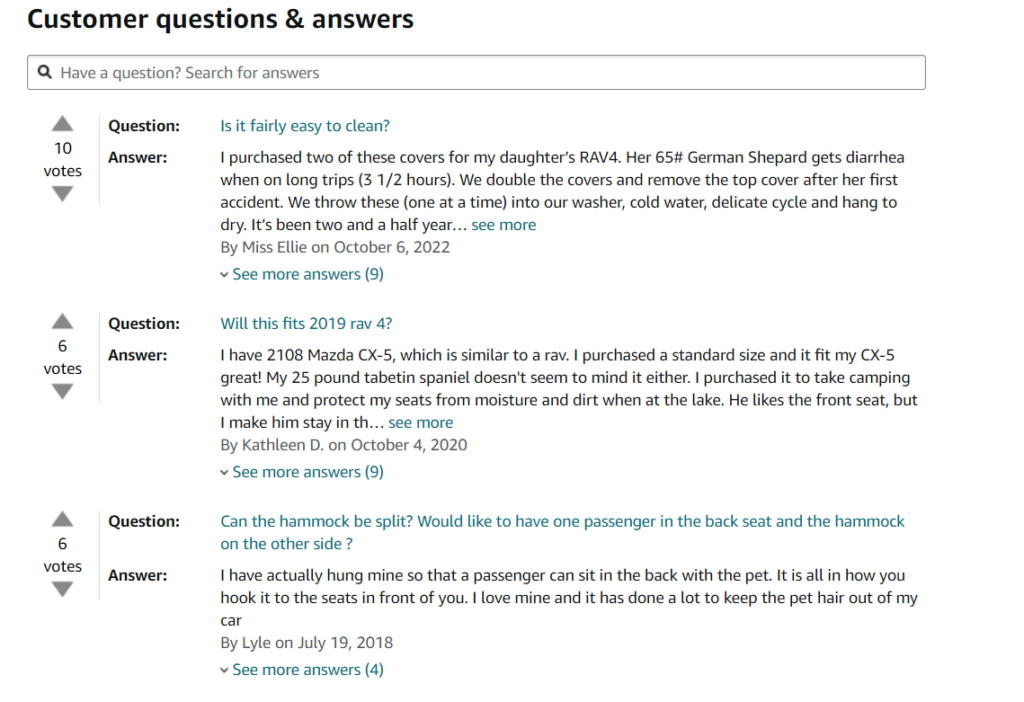
Repeat it for as many products as possible. It’s a goldmine. Answer all the questions in the best possible way. Remember, answer all the questions to solve the user’s problems. You can follow the same process on
- Quora
- Other Ecommerce websites,
But, please make sure your answers are unique.
Now the most confusing question is, where do you place FAQs? I like to place product-centric FAQs at the bottom of the product page.

You can also involve the developer for FAQ schema.
Step 2: Extracting generic question
Remember we installed the SEO minion? The same tool extracts generic questions from “people also asked questions” in SERP.
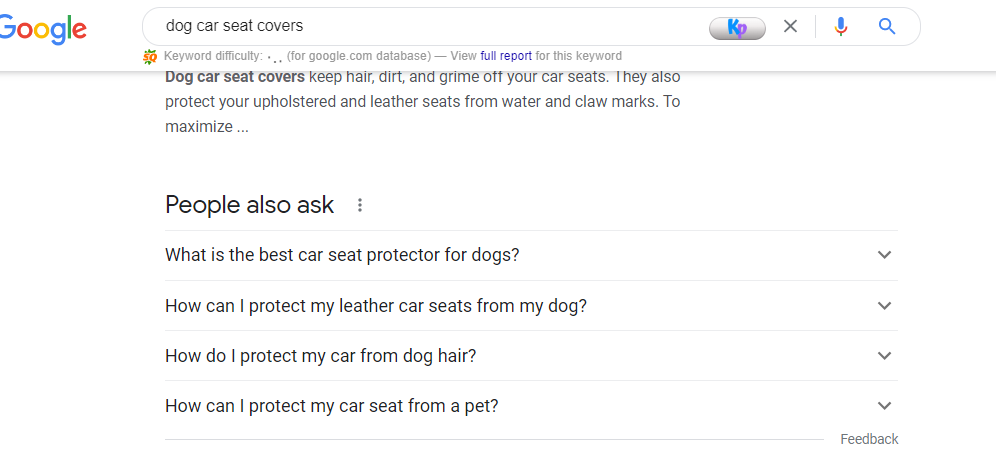
Select PAA levels and click on the Go button.
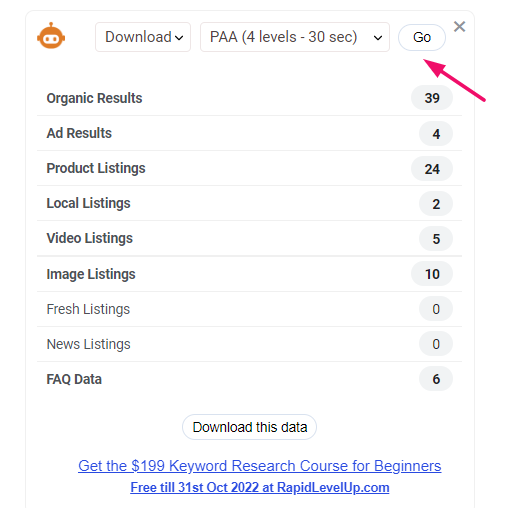
SEO minion will extract hundreds of questions within a matter of a few seconds.
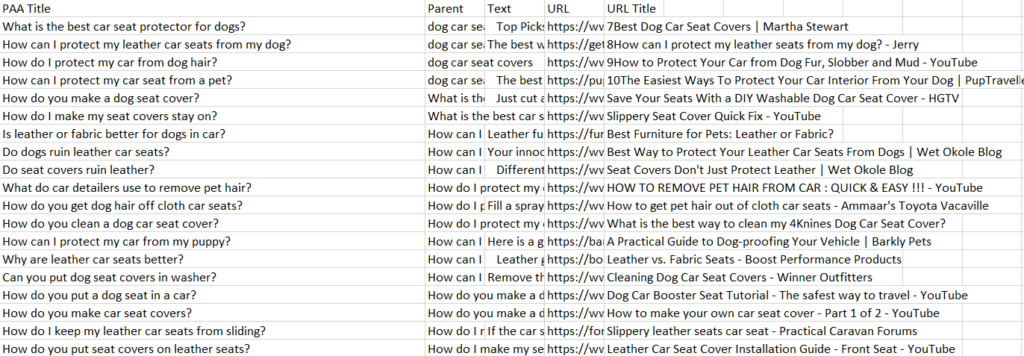
Many questions may look repetitive. You can either go through them manually and cluster them together or use clustering tools like KeywordInsights to cluster the questions with similar intent. It just saves you some time. 🙂
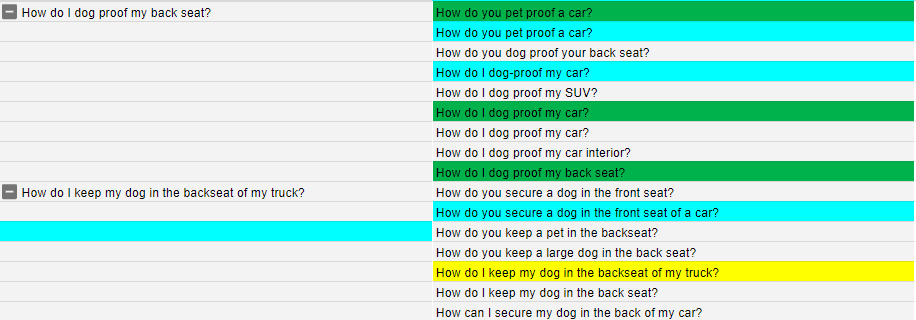
Now that you have the list of generic questions ready, you can start answering them. Since they’re generic questions, I like to make a separate post of them and link back to the product page.
Please note:
Internal linking is another essential product page optimization tip that occurs outside your product page. So you may not feel it’s necessary, but it is. So create as many posts of these questions and link back to your product page instead of putting all the content on your product page.
Tip #4: Write Unique Product Details
You don’t write on an eCommerce website to rank for one keyword. Even if you rank at the top for the primary keyword, it’s not necessary that you’d have the most traffic. Here’s the proof:
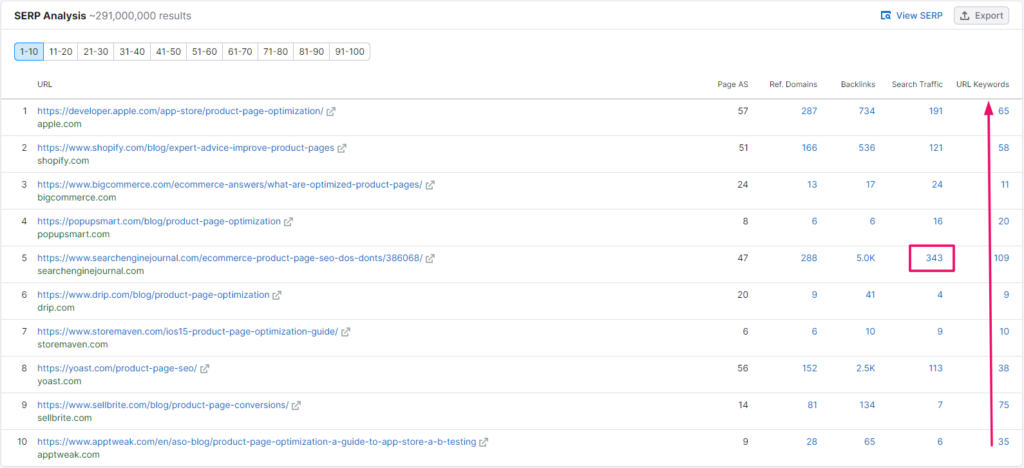
For the keyword “product page optimization,” the Search Engine Journal attracts maximum traffic. Why? Because they’re ranking for a maximum number of keyword variations.
If you keep product descriptions the same for all the product pages, you may rank at the top for some keywords but may not rank for variations and related keywords. So always write unique product descriptions for every single product page.
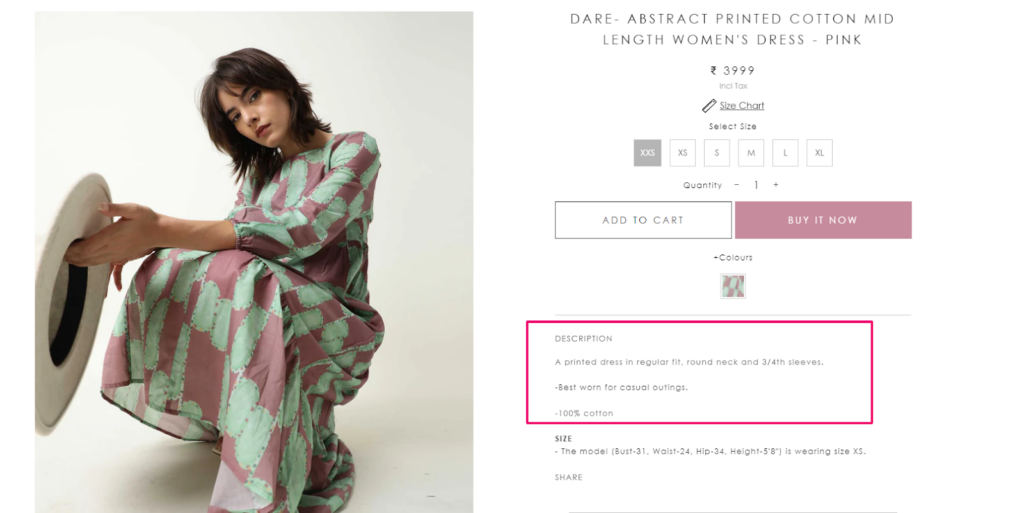
You may ask, should you have separate pages for products with multiple colors? Like Aristobrat pulls it up for their t-shirt range.
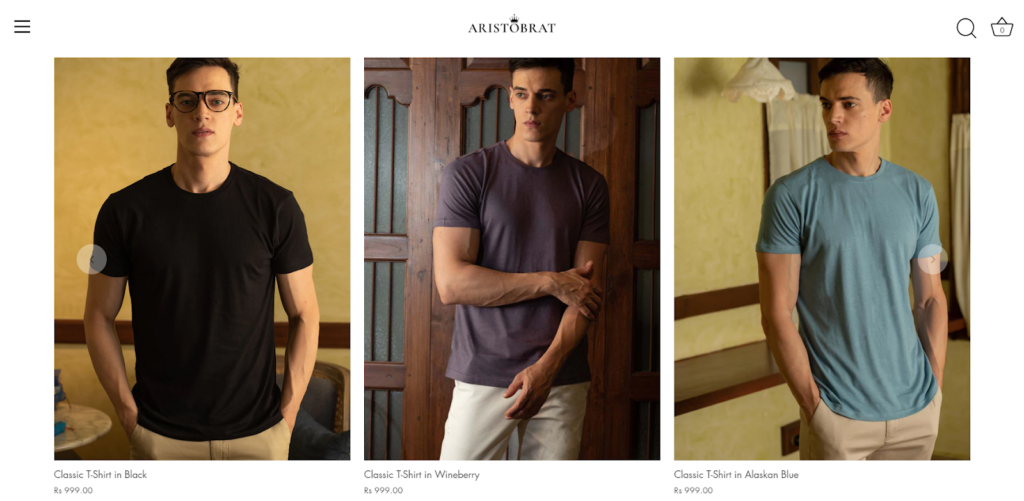

I believe it’s a huge part of product page optimization, and the answer will depend on the following criteria:
It’s only advantageous if:
- visitors are searching your products with the color (way too many of them)
- there are enough sales for the particular (again, way too many of them)
I strongly suggest you have the colors on one single product page unless your products meet the above criteria. If they do, don’t forget to have unique product descriptions. Aristobrat uses the same description for all the pages. Something I am not a big fan of. But it may have been working for them. Keep yourself open to tests.
Tip #5: Include Product Reviews & Get Social Proof
I love executing product reviews for two reasons.
- First, you make your customers the product evangelist.
- Second, you get a very good conversion.
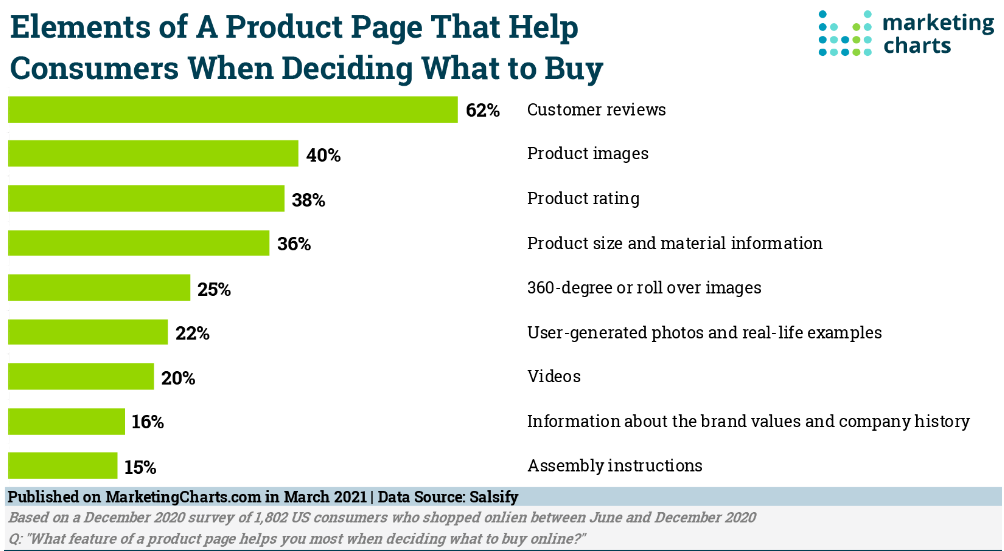
You can apply two short and sweet strategies I use to collect product reviews and use them for more conversion.
Step 1: Collect reviews
I use Kudobuzz to collect bulk customer reviews.
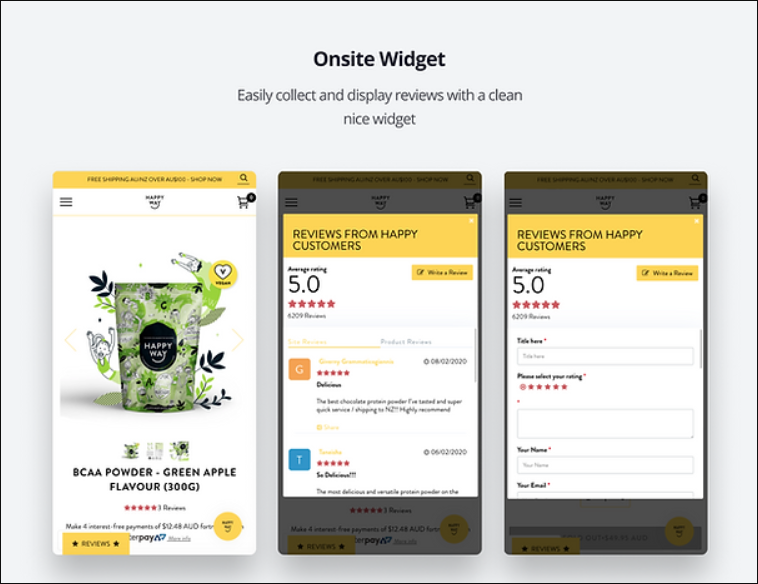
The app allows me to
- display reviews on the product pages
- send automated emails for customer reviews
- index all the reviews by search engines
What I like the most about Kudobuzz is it allows you to convert negative reviews into positive ones by letting you engage with the reviewers at a personal level.
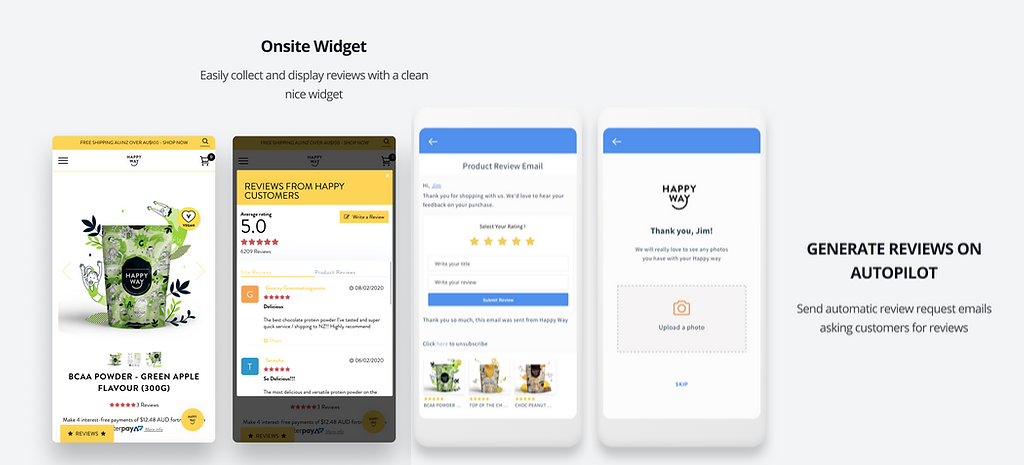
Step 2: Place customer reviews closer to the CTA
Now that you’ve collected customer reviews, where do you place them? More than collecting, I feel placing them smartly is part of product page UX optimization.
Some like to keep a review schema for it.
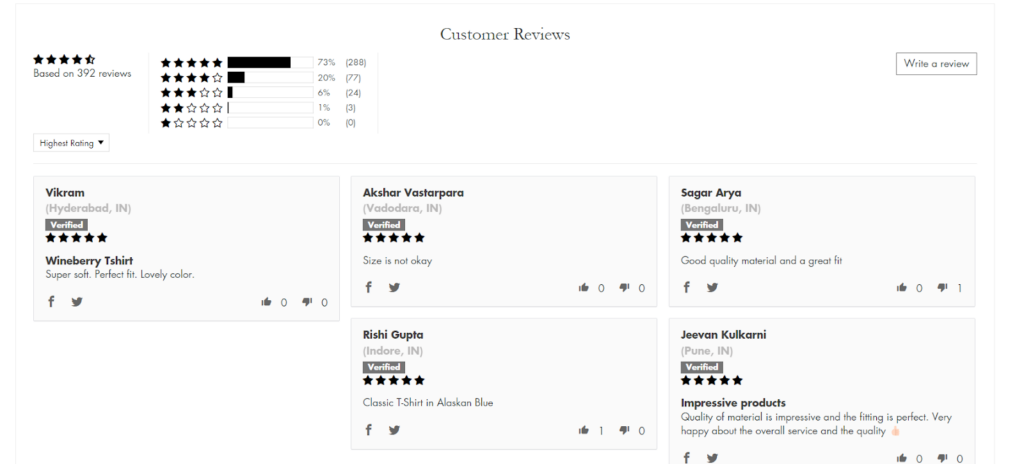
I do put the schema. But I have observed it’s always good to keep additional reviews near the CTA as well. When you place the reviews near the “buy now button,” users get confidence from past purchases.
Isn’t it simple, yet looks promising?
Tip #6: Optimize All Media Types
Product images, and videos must be clean, focused, and high-resolution. That’s obvious these days. But that’s not it. My favorite type of product page media optimization is using product images in scale.
Step 1: Use product images in scale
Let me show you an example.
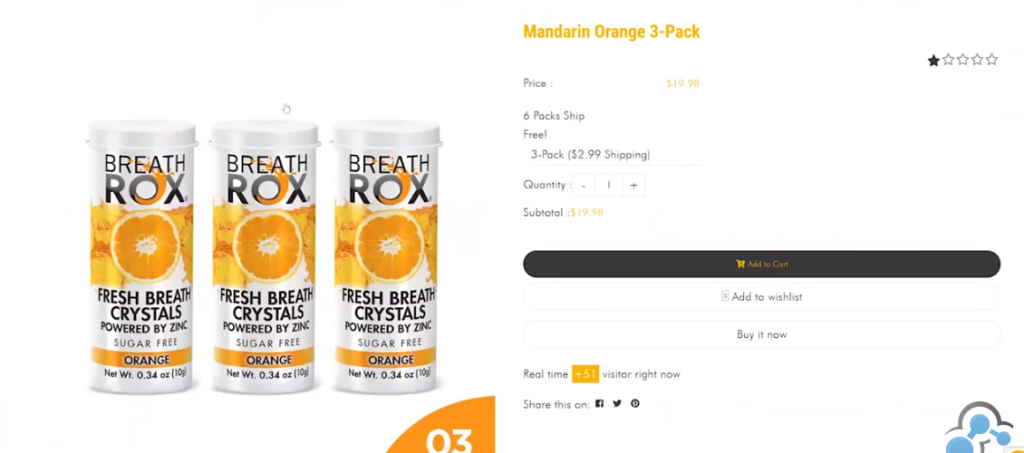
and
So in the first image, the visitors may not know the size of the can. Maybe they’re expecting bigger cans because of the image. But if you check the second image, there’s hardly any cloud of doubt.
It’s a small psychological technique, but
- you’re setting up clear expectations for the users
- you have fewer returns
Step 2: Use at least five images
Capture product images from all angles. Make a point that your product is excellent from all the points.

Step 3: Image zoom
Allow your users to zoom the product images for clarity. You’re not only optimizing the product page but optimizing the user journey on the product page.

Step 4: Put a product video
- 97% of eCommerce video marketers believe videos increase product understanding for the users.
- 76% of video marketers report product videos shooting up sales,
So using a product video is more of a widely accepted approach now.
Step 5: Feature customer photos and videos
I feel it’s one of the underrated product page optimization techniques. You want to have photos and videos of real people using your product.
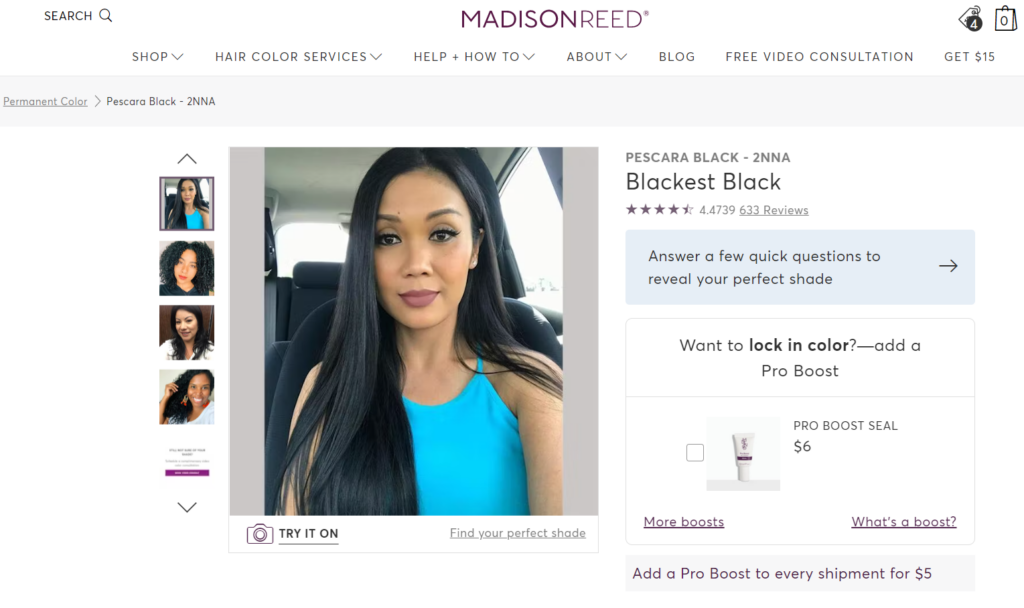
Madison Reed picks user-generated content from Instagram. Now featuring all the UGC on your product page can be a task if you try to gather all of them yourself. A more innovative way is to use tools like Statusphere.
The app sources and asks for permission from customers to use the images on product pages and emails.
Tip #7: Speed Up Product Pages
To speed up the product page, consider optimizing every element that’s visible on the product page. There Are multiple ways to reduce the page load time, but I will discuss the ones I religiously practice.
Practice 1: Check average page speed on Google Analytics
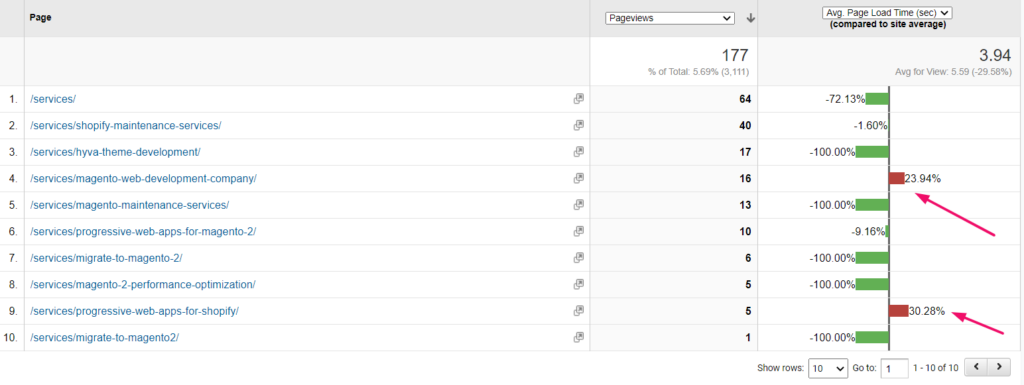
Find the product pages with an average page load time lesser than the site average. Work on those pages.
Practice 2: Measure the speed on GTmetrix
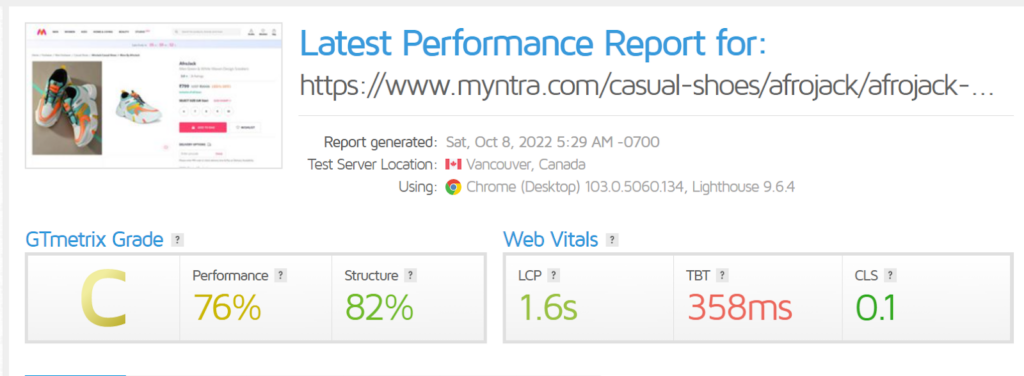
Focus on the non-performing metrics and work on improving them.
Practice 3: Optimize product images
Media files affect the loading of the product page. I usually keep all my images in the Google-recommended WebP format. I also compress the images using Imagify.
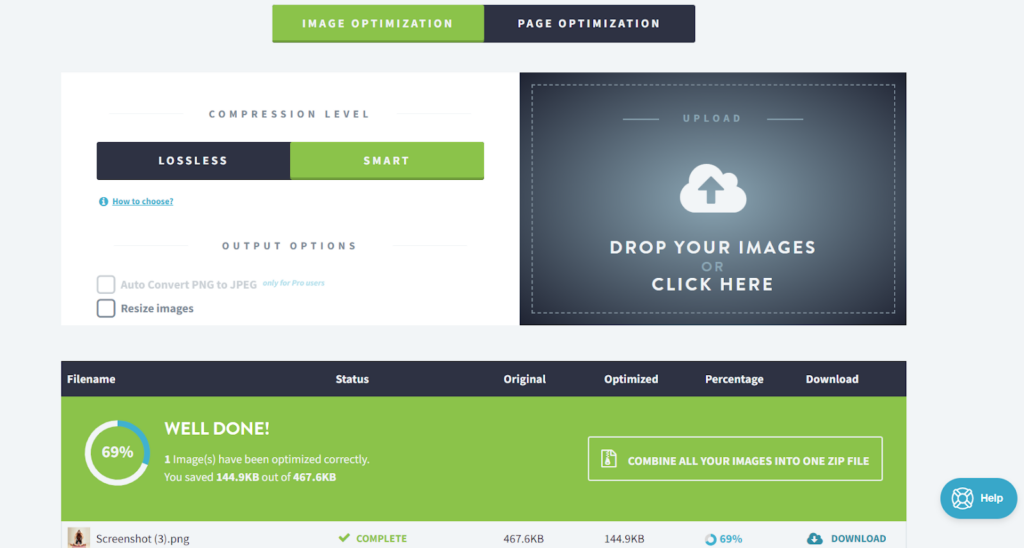
You also have the option to retrieve all your images from the product page and launch the page optimization.
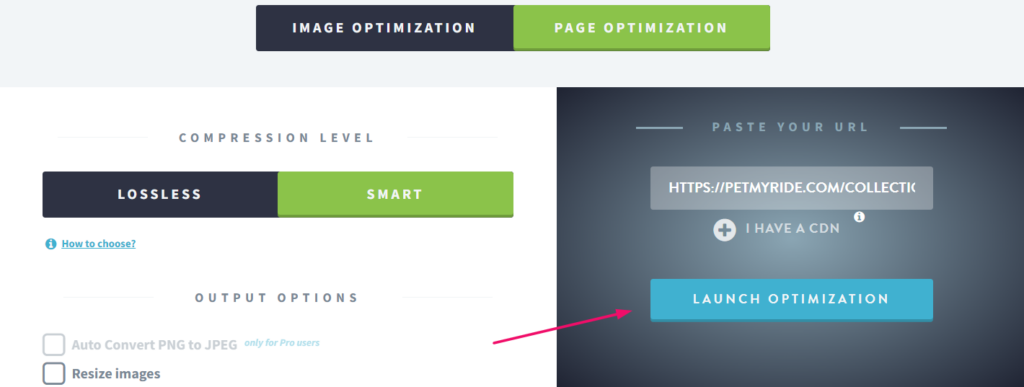
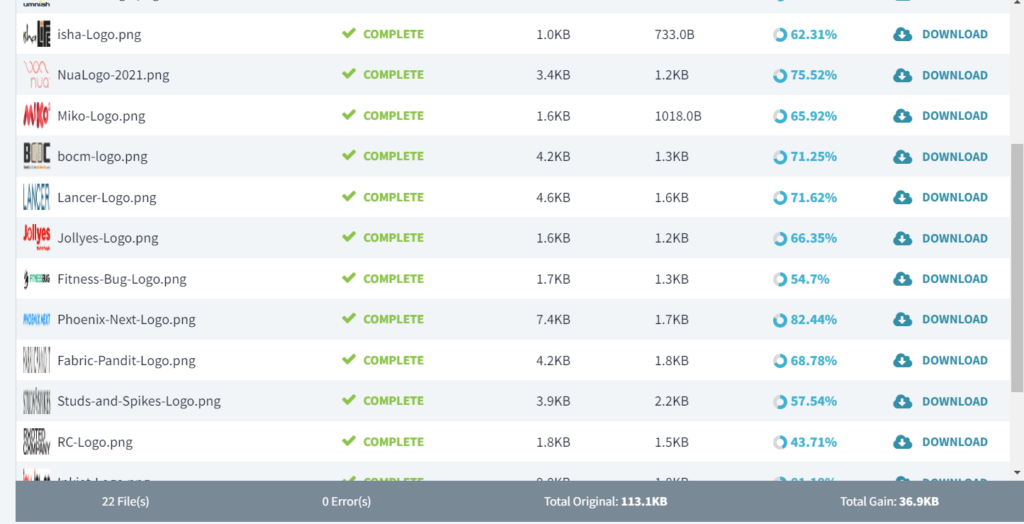
See how Imagify pulls out all the images from the uploaded files and minifies them.
Other methods to speed up your product pages
- Disable all the unused plugins
- Host Google fonts locally
- Optimize third-party resources
- Clean your unused database
- Upgrade to the latest PHP version
- Use speed booster plugins like Nitro
Tip #8: Focus On Product Availability
One of the issues while dealing with products is they get out of stock and, sometimes, even get discontinued.
The issue just amplifies when the product page attracts traffic. In such cases, it’s difficult to decide whether you want to keep the page live or not.
Step 1: For discontinued products
What I usually do with such pages is I put a “Product no longer available!!” message, followed by a navigation link to a similar product.
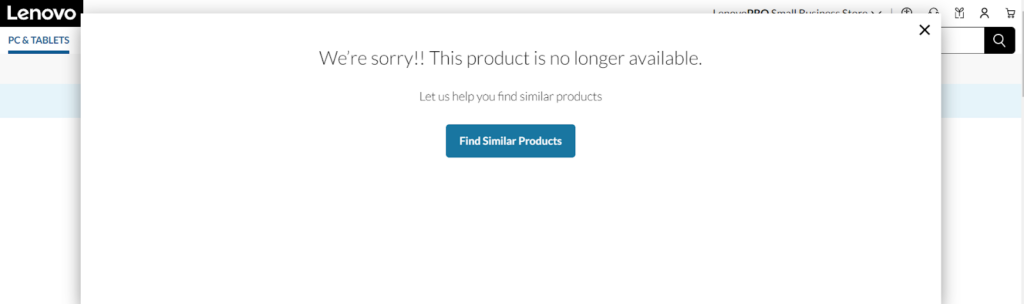
This way, you’re neither deindexing nor removing the page.
Another good practice for discontinued products is to clearly state on the product page.

Step 2: For Out-of-Stock products
I don’t do anything differently for out-of-stock products. Either I incentivize users to increase conversion on out-of-stock product pages. Or I guide them to alternative products.
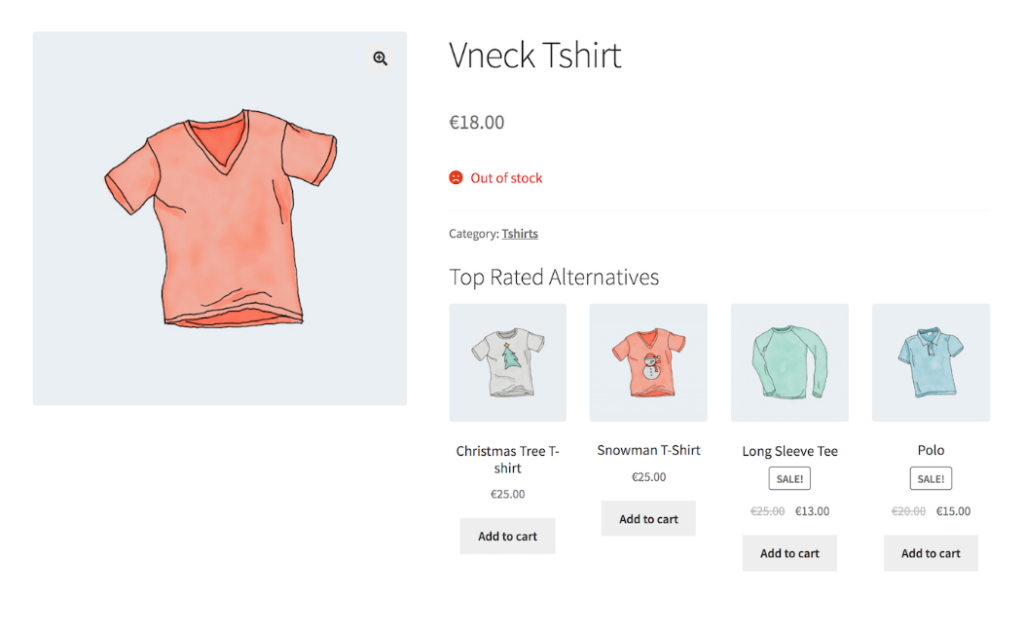
Source: WooCommerce
Some intelligent marketers make opportunities out of disaster. They pull up out-of-stock pages as an email collection tool. This is more of a design optimization process, but extremely important.
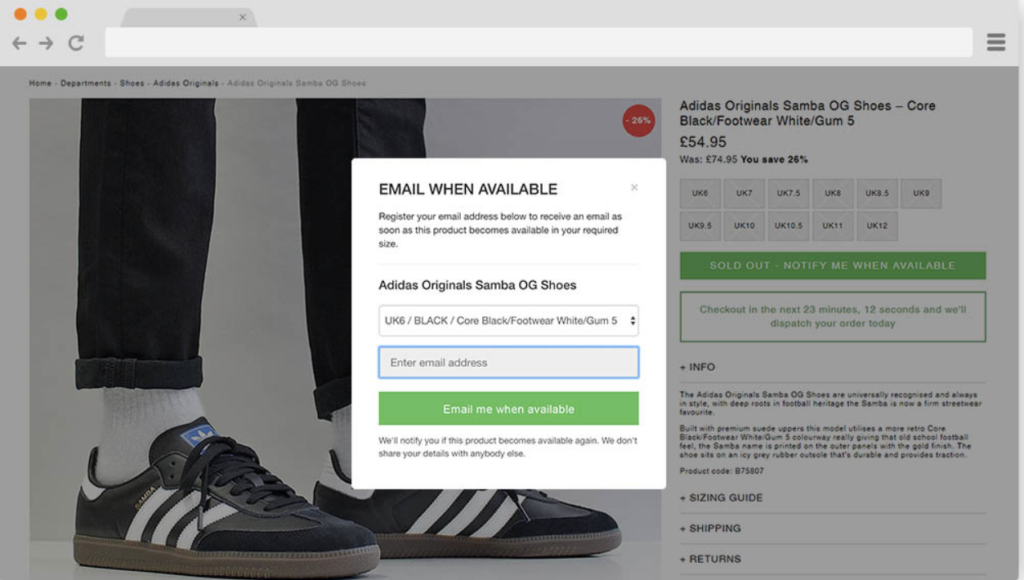
I observe another masterstroke most brands play. “Bury the products at the bottom of the load pages.“
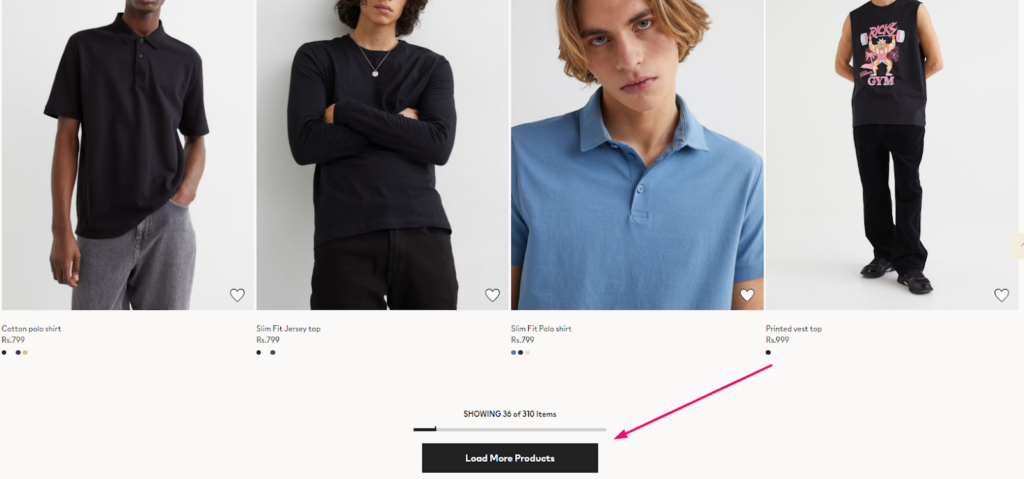
You’ll do this on the product category page. But it’s a good practice that helps your product pages as well.
Tip #9: Avoid Manufacturer’s Product Descriptions
It’s a short and simple tip. Avoid product descriptions from manufacturers. It will create a duplication issue.
You want to make your description:
- easily digestible
- benefit-oriented
- crisp and meaningful
- original
- actionable
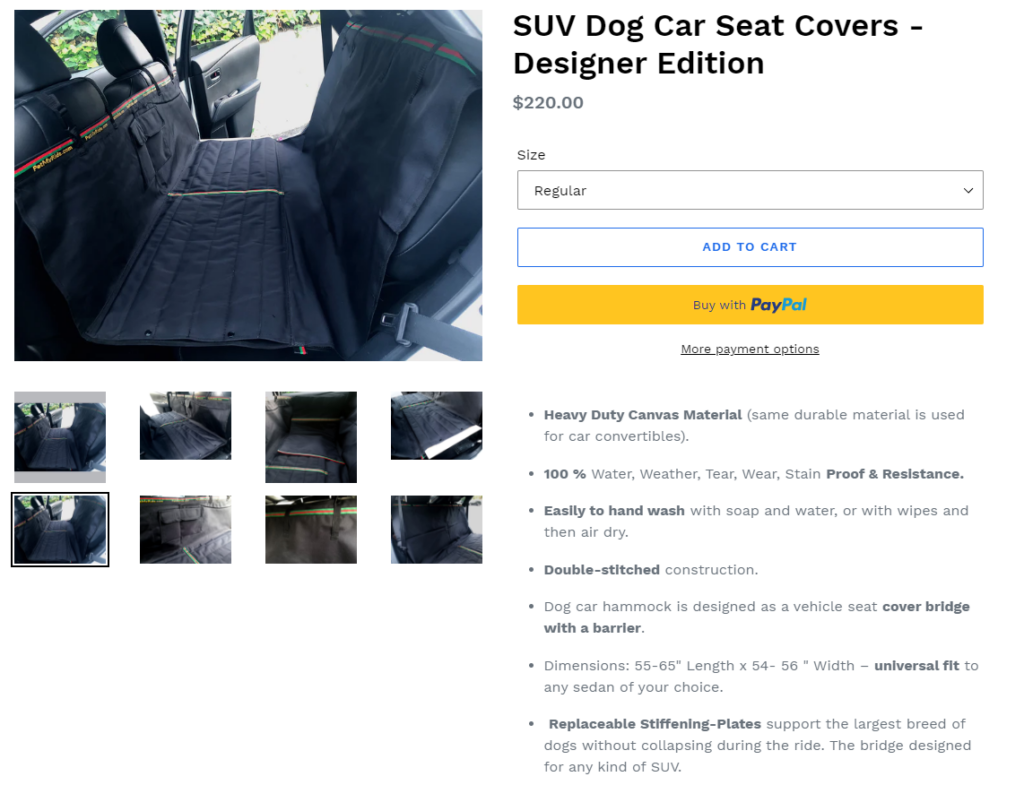
Tip #10: Audit Technical Issues On Your Product Pages
This is something important and hard to execute. And the technical audit checklist itself needs a separate blog. So I will focus on some of the easily solvable problems.
Solution 1: Fix duplicate title tags and meta descriptions
I use Screaming Frog to find duplicate title tags and meta descriptions.
- First, crawl your website on it.
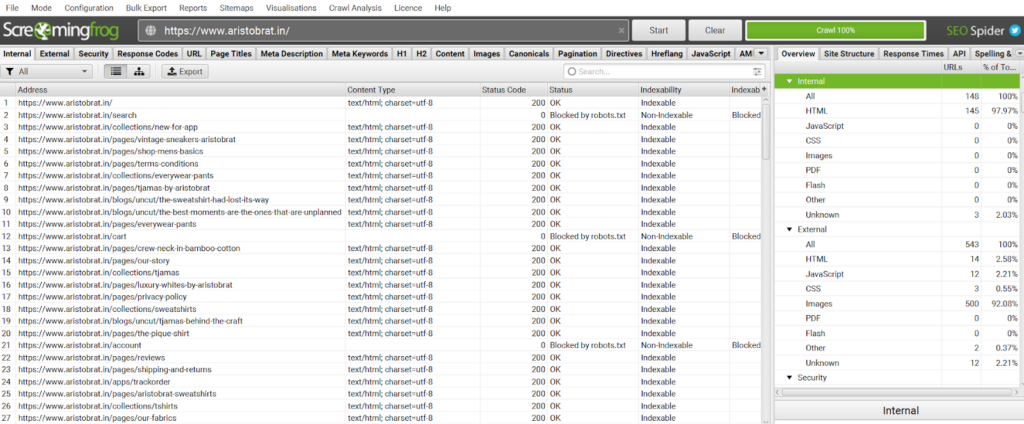
- Go to Page Title >> Duplicate on the right corner
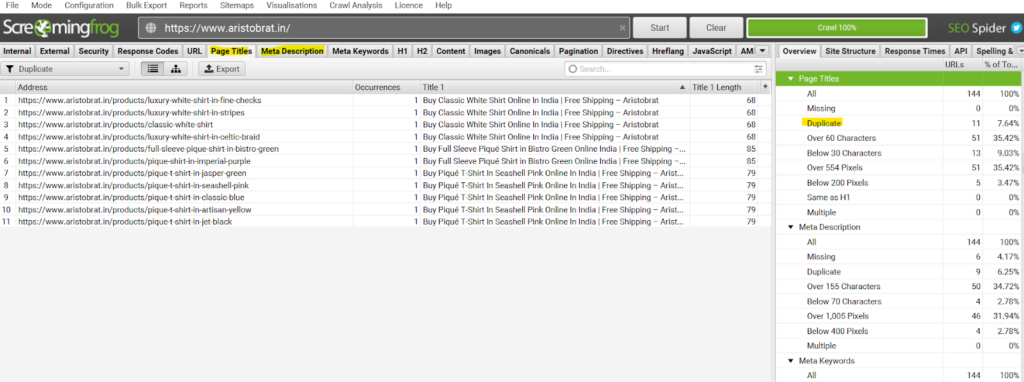
Make the titles unique. You don’t want to confuse Google with the same tags. Apply the same technique to meta description and headings to make all the pages unique.
Solution 2: Fix broken links
You want to find all the in-links and the out-links that’s broken (not accessible). Again, it’s pretty easy to execute.
- Go to any product page on Screaming Frog
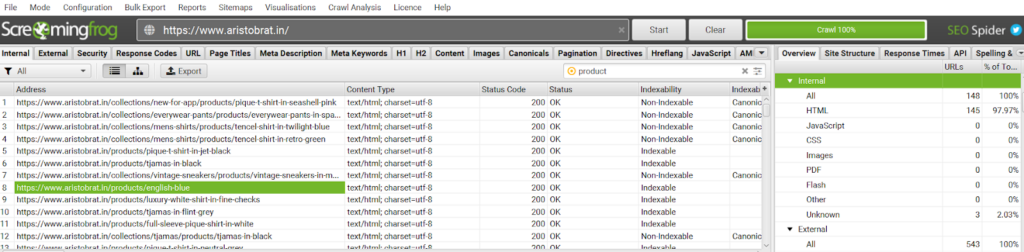
- Scroll down to in-link and out-link section at the bottom
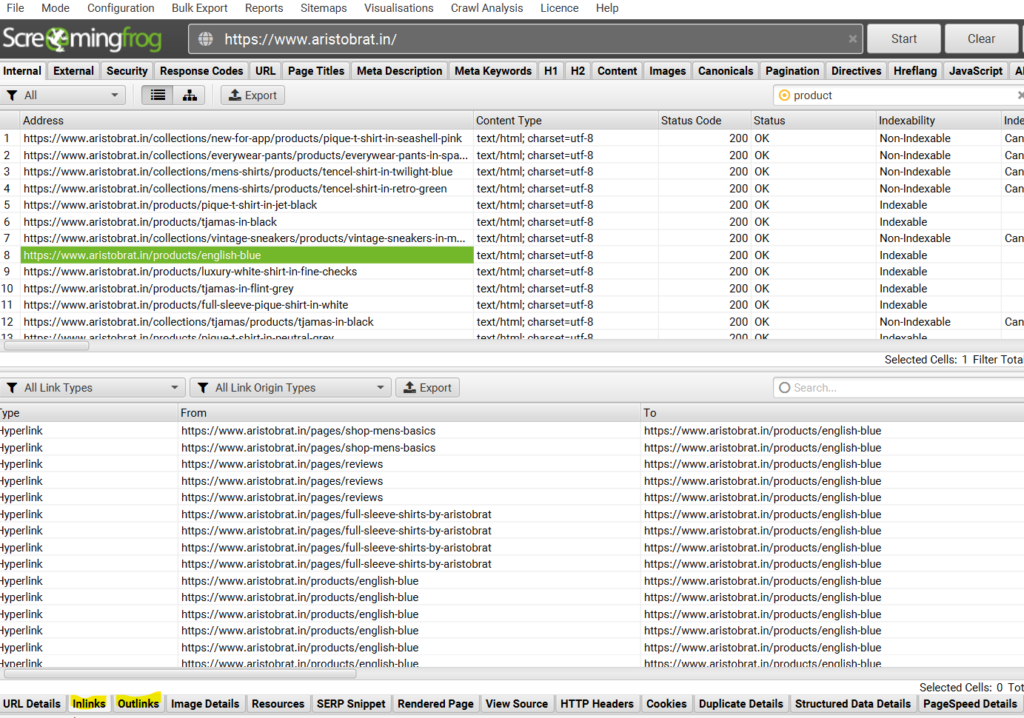
- Scroll right to status code & find all the 404 pages
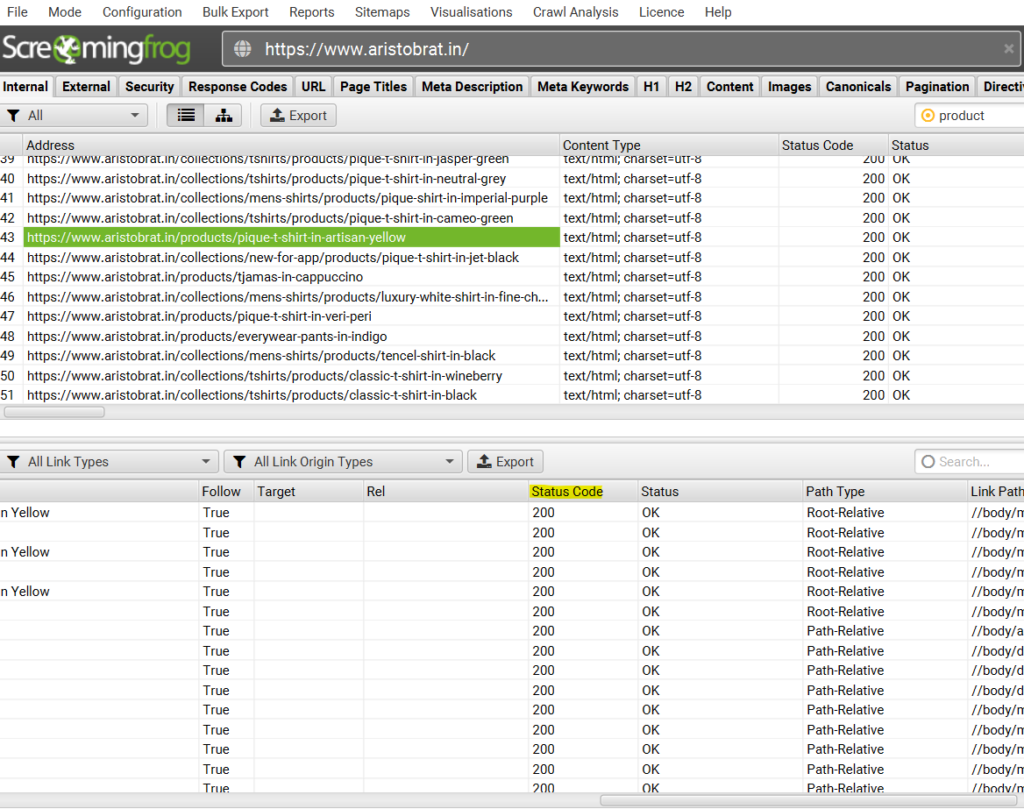
- Add all the relevant pages to the broken links
Solution 3: Use only one H1s
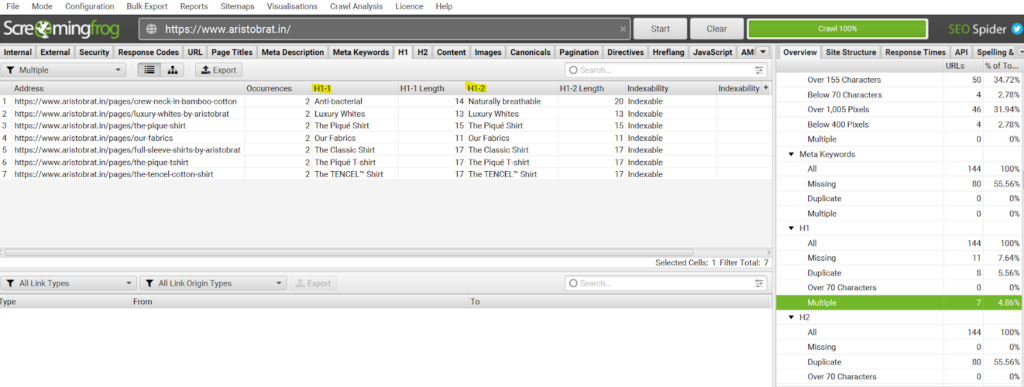
Again, it’s simple to diagnose multiple h1s for any product page. Find all the multiple h1s occurrences in the h1 tab.
H1>> Multiple
Solution 4: Low content product pages
What I like about screaming frogs is that they also suggest pages with low content quality. Pages with fewer word counts are put in this category.
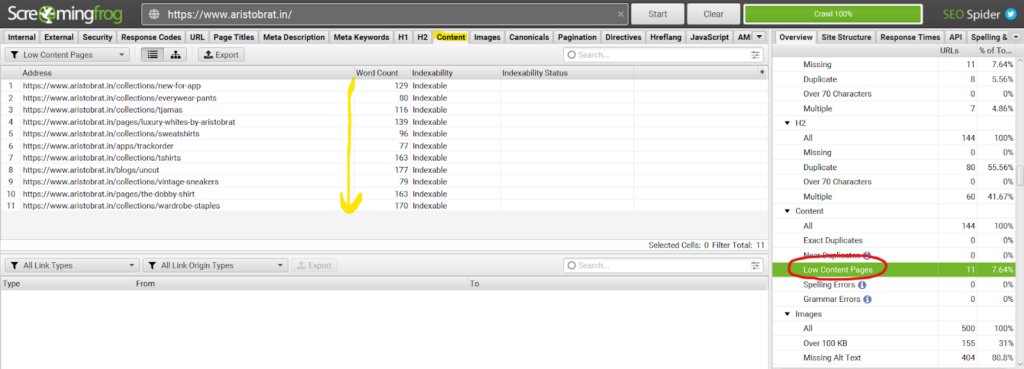
You can start writing more content on these pages. I manually go through each page and check if the page deserves more content.
You can identify other problems, such as
- Missing structured data
- Pagination
- Canonicals
- Javascript issues,
But I recommend hiring an expert to suggest and resolve these errors.
Tip #11: Use MarkUp Schema On Product Pages
Well, I’d say this is the toughest of all to execute. But if you use structured data for your product pages, Google will show the information more richly on SERP.
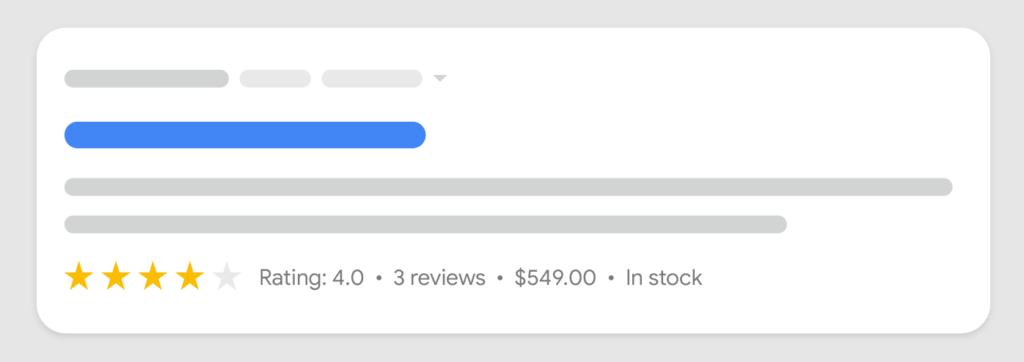
Source: Google Search Central
Source: Google Search Central
Rich product result pages get more CTR and traffic.
Read: How to add product structured data
Tip #12: Test The Product Pages
The tips I shared with you’re not hard-scribed texts on stone. I have tested them on Google Optimize and SEOTesting and found them relevant. You can test the impact of any element through A/B or Multivariate testing.
I usually conduct A/B testing using Google Optimize. Here’s how to create your testing experience for the product pages on Google Optimize.
Step 1: Create New Experience & Fill in The Details
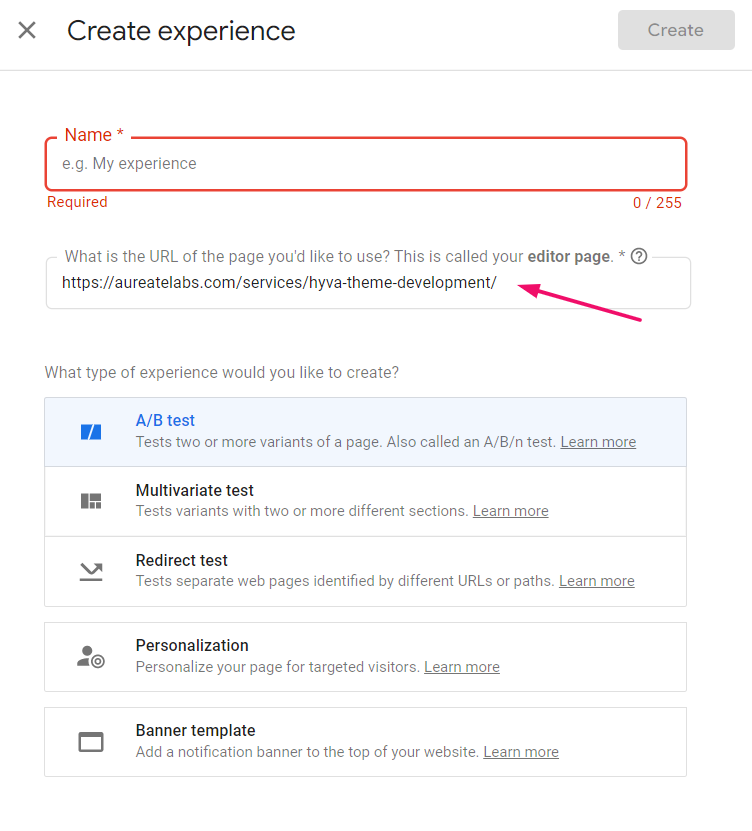
Click on A/B testing if you only want to test one change.
- Color of the bottom
- Placement of the button
- Heading
- Product descriptions
If you have test variants with two or more different sections, go with the multivariate test.
Step 2: Edit a variant page
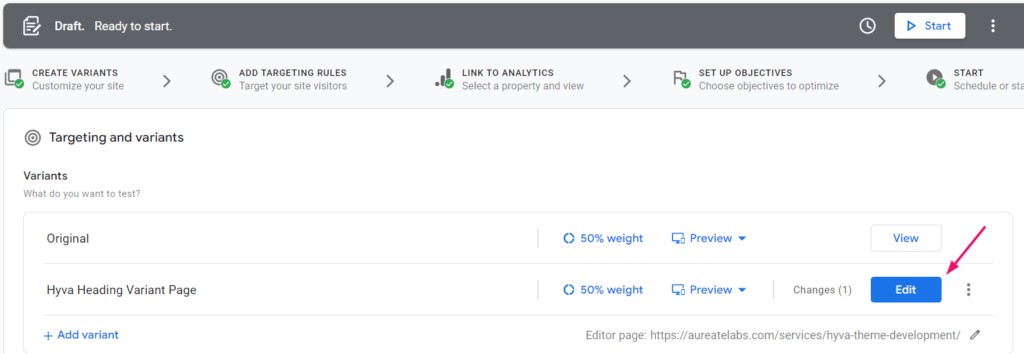
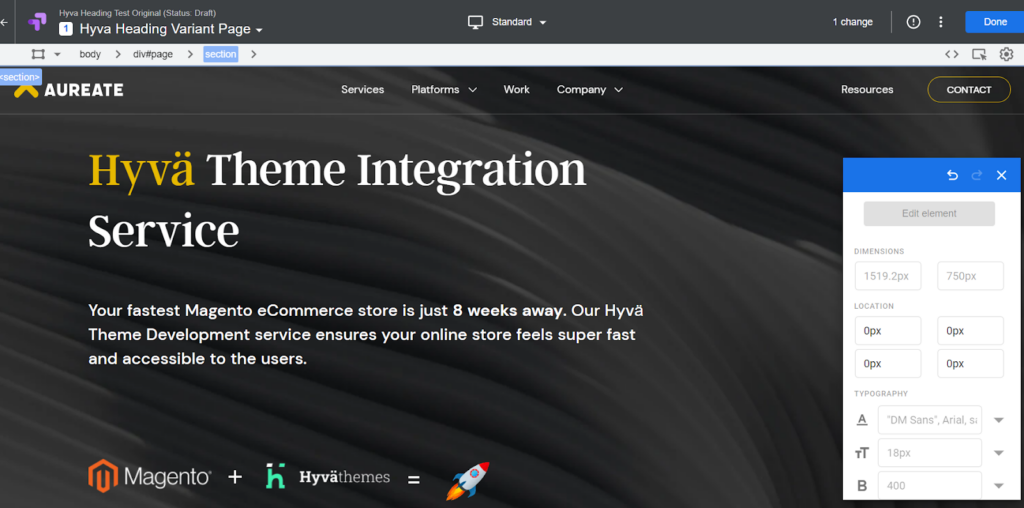
Step 3: Make changes
Google Optimize will come with its editor. You can make changes to the product page without going to the backend.
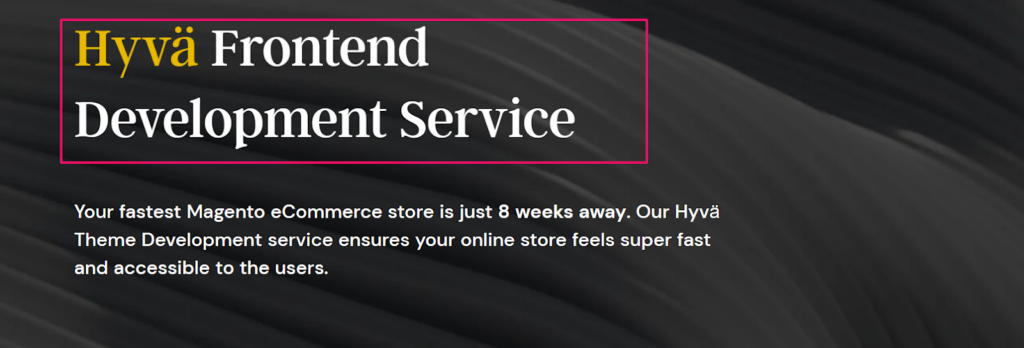
Step 4: Compare original vs. variant page
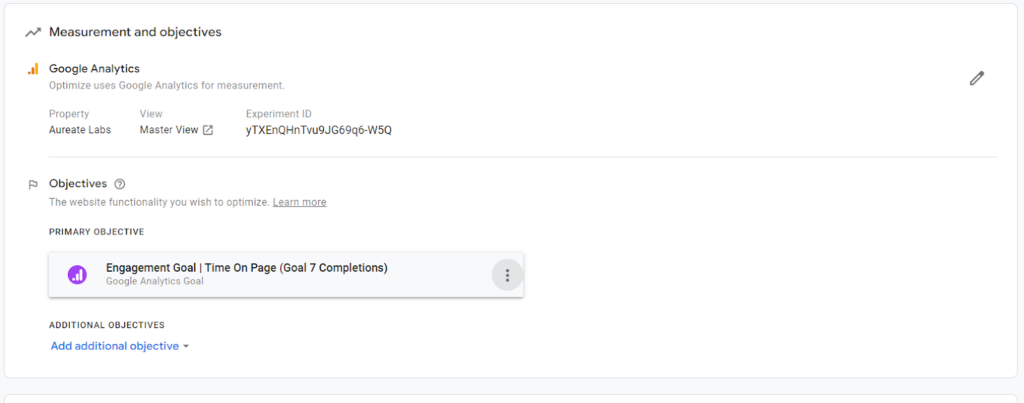
Step 5: Add primary objectives
Add objectives (goals from GA) you want to track. It can be any goal you’ve already created on GA.
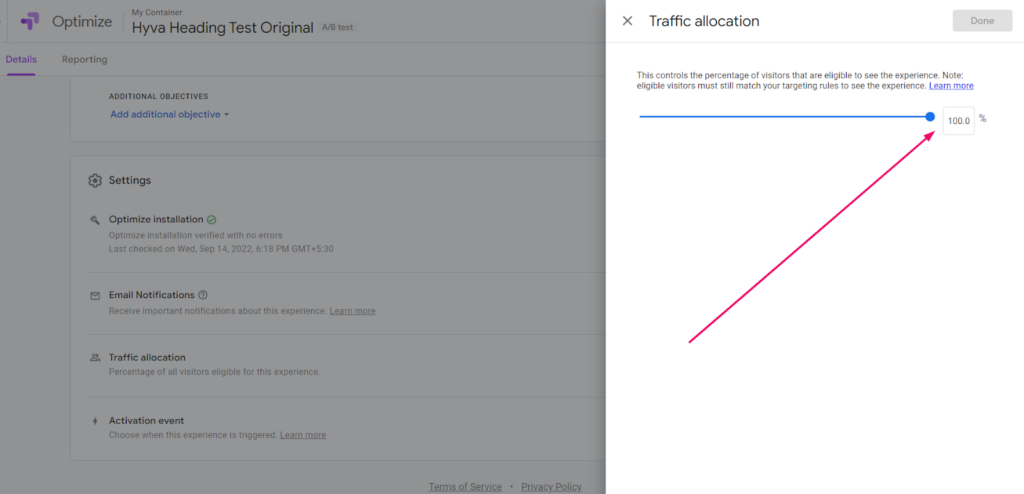
Step 6: Allocate the traffic & enjoy the results
Distribute the traffic across the original and variant pages.
You can create such tests for your product pages and observe the results. As I always say, optimization is not science. It’s not facts. It’s testing! And different tests under different conditions will produce different results.
How To Measure The Impact Of Product Page Optimization?
Now that you’ve optimized the product page, you want to measure the impact. Testing is a good way to keep track of how your page performs. But what should you track when Google Analytics looks so overwhelming and intimidating?
Don’t worry! Most organizations track only 3-5 goals and subsequent KPIs. You can measure the impact of optimization on your product pages by measuring:
KPI #1: Daily, weekly and monthly unique visitors
It tells you about product page awareness.
- Go to analytics view
- Write all pages
- Select the pages based on content grouping
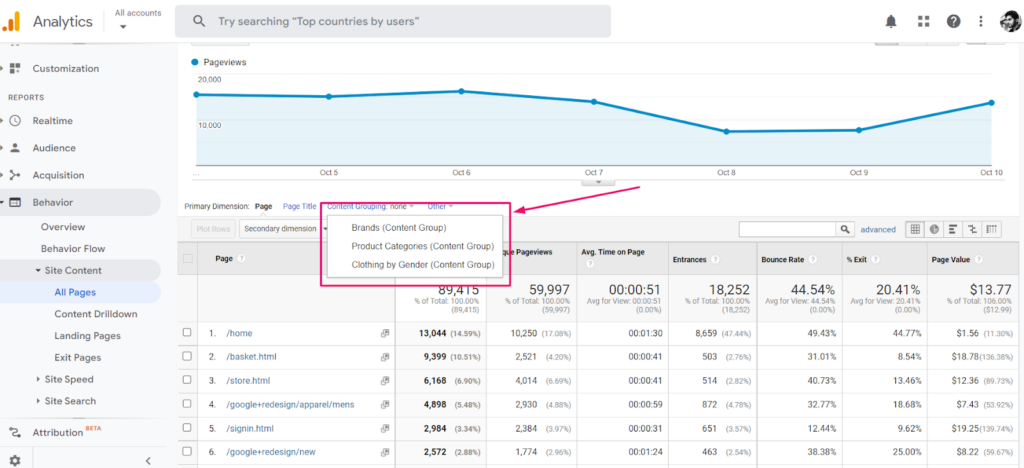
- Track all the product pages and look for monthly, weekly, & daily visitors
KPI #2: Active users
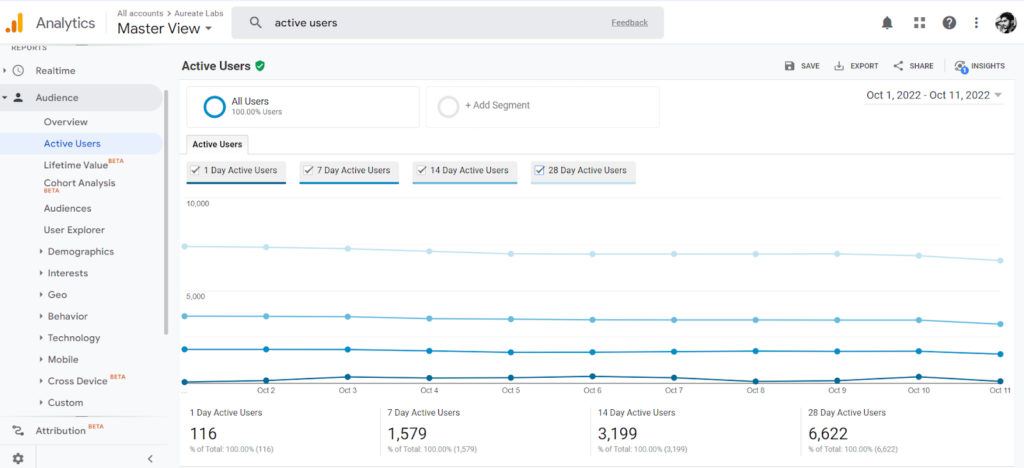
You can calculate the total active users’ report (unique users in the past 1, 7, 14, and 28 days).
The number tells how well you perform with unique users who started sessions on your site.
KPI #3: Average order value
If there’s an improvement in the average order value, the optimization is working.
You’ll find it in the conversion >> eCommerce >> overview section
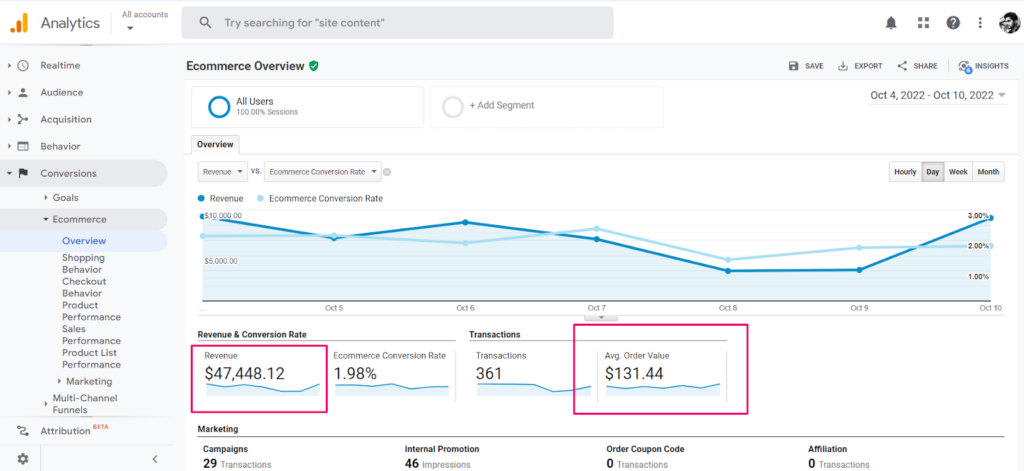
You can also calculate engagement and conversion by tracking goals.
If you want to track engagement on the product page, you can track
- Average time spent on the page
- Interaction with the buttons
Similarly, you can track checkout complete goals to determine if the optimization worked.
Conclusion
I’d say:
Be different. Be unique. And be everything that stands you out from the competitor. But keep an eye on your metrics. You can implement all the strategies I mentioned. But it wastes your time if you’re not tracking your eCommerce product pages.
I feel I can’t define the most important metrics for you. It can be referral traffic, social traffic, or conversion rates. But whatever you pick, track it for a good period to interpret any meaningful data from it.
Feel free to suggest any secret tips you use that have worked the best for you. I’m always listening. 🙂 Also, we’re going to bust many secrets in our coming chapter on optimizing images for the web so you can implement all the tips on your store without relying on “experts.”
Frequently asked questions
Here are some questions related to product page optimization.
Product page optimization is the process of optimizing every element on the product pages. Hence, the pages are easily discoverable, crawlable, indexable, & understandable to search engines and are informative and effective enough to convert visitors into buyers. An optimized product page also meets search intent & has high transaction value.
You can optimize a product detail page by
1. Start with serious keyword research
2. Optimize title tags
3. Add product-related faqs
4. Write unique product details
5. Include product reviews & get social proof
6. Optimize all media types
7. Speed up product pages
8. Focus on product availability
9. Avoid manufacturer’s product descriptions
10. Audit technical issues on your product pages
11. Use mark-up schema on product pages


