What is an E-commerce Website: A Complete Guide (2026)

Gone are the days of limited hours and crowded stores. The way we shop and do business has significantly shifted in recent years. Customers can shop anytime, anywhere, from the comfort of their homes or on the go over the internet, and E-commerce makes it happen.
By 2026, global e-commerce sales are projected to reach $8.5 trillion. In the U.S. alone, the market is predicted to grow by 43.58% between 2024 and 2028.
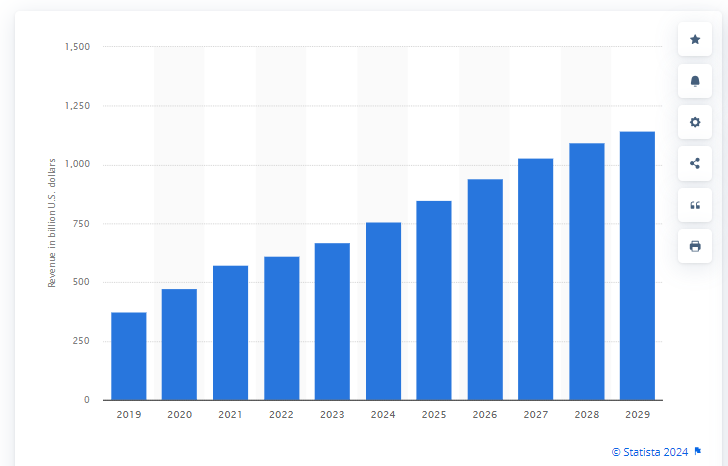
This convenience isn’t just a passing trend. With over 5 billion people now using the internet globally, the online marketplace has become vast and accessible for businesses and consumers.
In this comprehensive guide, we will look at what e-commerce websites are, how they work, why they matter, and much more. Let’s get started.
What is an E-commerce Website?

E-commerce website is a digital storefront that enables businesses to sell goods and services over the Internet. It’s a platform that’s open 24/7, allowing customers from all over the world to shop at their convenience.
Amazon is a prime example of an e-commerce website. It’s a platform where millions of products are available for purchase, from books and electronics to groceries and clothing. Customers can browse through a vast array of products, read reviews, compare prices, and make purchases, all from the comfort of their homes.
What are the Types of E-commerce Websites?

Various types of e-commerce websites have emerged to cater to different business models and consumer needs. Each type has its unique features and requirements, and businesses must choose the model that aligns with their goals and customer needs.
Business-to-consumer (B2C)
B2C websites are the most common form of e-commerce. These platforms sell products or services directly to consumers. Examples include online retailers like Amazon and Walmart, which offer a wide range of products from electronics to groceries. B2C e-commerce is characterized by quick purchase cycles and, often, lower order values compared to B2B.
Business-to-Business (B2B)
B2B e-commerce websites facilitate transactions between businesses. They typically involve wholesale distributors or manufacturers selling to retailers or other businesses. These platforms often require features like bulk pricing, tiered pricing, and the ability to handle complex shipping arrangements. Alibaba and ThomasNet are prominent examples of B2B e-commerce websites.
Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)
C2C e-commerce platforms enable transactions between individual consumers. These websites often act as intermediaries or facilitators for peer-to-peer sales. eBay and Etsy are prime examples, allowing users to sell goods directly to other consumers. C2C websites must focus on user trust and security due to the direct interaction between buyers and sellers.
Consumer-to-Business (C2B)
C2B e-commerce reverses the traditional business model by allowing individuals to sell products or services to businesses. This can include freelance services, stock photography, and crowdsourcing platforms. Websites like Upwork and Shutterstock exemplify the C2B model, where businesses seek the services or products offered by individuals.
Business-to-Government (B2G)
B2G e-commerce websites are less common and involve transactions between companies and government agencies. They typically provide goods or services that support government operations, such as infrastructure projects or office supplies. These platforms may require adherence to specific regulations and often involve long sales cycles.
Government-to-Business (G2B)
G2B platforms facilitate interactions from government bodies to businesses. They are used for procurement, licensing, and other government-related business operations. These websites help streamline processes that would otherwise be cumbersome and time-consuming.
Government-to-Citizen (G2C)
G2C e-commerce websites are designed to provide services directly to citizens, such as renewing licenses, paying for utilities, or filing taxes. These platforms aim to increase the efficiency of service delivery and improve the accessibility of government services.
Social Commerce
Social commerce is an emerging trend where social media platforms integrate e-commerce capabilities. This allows users to make purchases directly through social media apps, streamlining the path to purchase and leveraging the platforms’ vast user bases.
Subscription E-commerce
Subscription e-commerce websites offer products or services on a recurring basis. This model has gained popularity in various niches, from meal kits like Blue Apron to streaming services like Netflix. Subscription models focus on customer retention and lifetime value.
Multi-channel E-commerce
Multi-channel e-commerce involves selling through multiple online channels, which can include a combination of B2C, B2B, and even brick-and-mortar stores. This approach maximizes reach and caters to customers’ preferences for various shopping experiences.
What are the Types of E-commerce Sales Channels
E-commerce sales channels are the pathways that businesses use to reach customers and sell their products. In 2026, the diversity of these channels is vast, offering multiple touchpoints to reach and engage with customers.
To maximize online presence, businesses need to understand the different types of e-commerce sales channels:
1. Online Marketplaces
Online marketplaces are platforms where multiple merchants can list and sell their products. These channels provide a broad audience reach and are often favored by consumers for their convenience and variety. Examples include Amazon, eBay, and Etsy. These platforms handle much of the traffic generation and have built-in trust factors, but competition can be intense, and control over branding is limited.
2. E-commerce Stores
E-commerce stores are websites owned and operated by a single business. They offer the most control over customer experience, branding, and product presentation. Shopify, WooCommerce, and Magento are popular platforms that enable businesses to create their own e-commerce stores. These channels require more effort in driving traffic and building customer trust but offer higher margins and customer loyalty.
3. Social Media Platforms
Social media platforms have evolved into sales channels with integrated e-commerce features, such as Facebook Shops and Instagram Shopping. These channels allow businesses to leverage their social media presence to sell directly to consumers within the platforms. The key advantage is the ability to use social engagement to drive sales, though it requires a strong social media marketing strategy.
4. Mobile Commerce Apps
Mobile commerce apps are dedicated applications for mobile devices that facilitate online transactions. They offer a streamlined shopping experience optimized for smartphones and tablets. Apps can increase customer loyalty through a convenient, fast, and personalized shopping experience, but they require significant investment in app development and maintenance.
5. Comparison Shopping Engines
Comparison shopping engines (CSEs) are channels that collect product information from various retailers and present it to consumers for comparison. Google Shopping is a prime example. These platforms are excellent for price-sensitive customers and can drive targeted traffic, but they require competitive pricing and often operate on a pay-per-click model.
6. Affiliate Networks
Affiliate networks connect businesses with affiliate marketers who promote products and earn a commission on sales. This channel can extend a business’s reach and is performance-based, meaning businesses pay for actual sales. However, managing affiliates and ensuring brand consistency can be challenging.
7. Dropshipping Platforms
Dropshipping platforms allow businesses to sell products without holding inventory. When a customer places an order, the product is shipped directly from the supplier. This model reduces overhead but offers less control over shipping and product quality.
How Does an E-commerce Website Work as an Online Store?
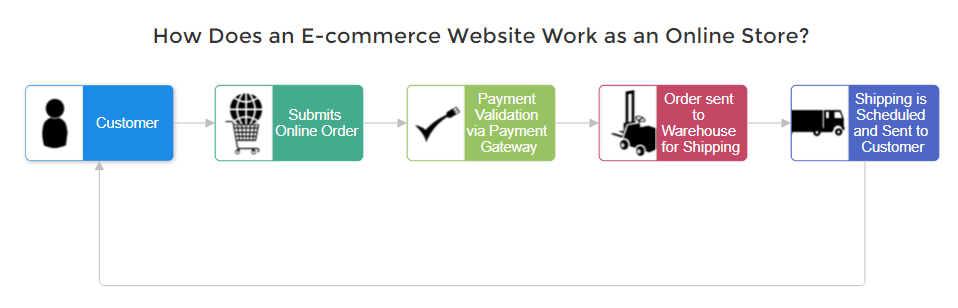
E-commerce websites function as virtual storefronts, meticulously designed to replicate the in-person shopping experience.
In an online store, businesses rely on technology and digital platforms, including website builders, mobile apps, and social media, payment gateways to make transactions possible. They can be accessed anywhere with an internet connection. Here’s a breakdown of the key processes:
- The business creates the website and lists the products or services for sale, providing detailed descriptions, prices, and images.
- Customers find the website, browse through the listed products or services, and select the ones they wish to purchase.
- Customers move to the checkout phase, where they provide necessary payment and shipping information.
- The e-commerce website sends the payment information through a payment gateway, which approves or declines payment based on whether the funds are available.
- After the payment is validated and collected, customers receive an order confirmation and purchase receipt.
- The backend system updates inventory and prepares the order for shipment.
- The order is shipped to the customer with tracking information provided.
- The customer receives the order completing the transaction.
- Post-sale customer support is provided to handle any issues or queries that the customer might have regarding the product or service.
With its combination of functionalities and processes, an e-commerce website makes shopping easy. While the process may seem simple on the surface, there are many moving parts to coordinate for all online purchases. Let’s look at what an effective e-commerce website should do.
What Should An E-commerce Website Do?

The primary function of an e-commerce website is to provide a seamless and secure online shopping experience, from product selection to checkout. E-commerce websites must integrate many key components to deliver a seamless user experience. Here are the things they should do:
Product Catalog
A cornerstone of any e-commerce site is its product catalog. This should be:
- It must include detailed listings of all products, complete with high-resolution images, specifications, prices, and availability.
- A robust search function with filters allows customers to find products quickly.
- The catalog should update in real time to reflect changes in pricing, availability, and product options.
Shopping Cart
The shopping cart is a critical component that:
- It should allow customers to add multiple items and edit their selections before checkout.
- It must automatically calculate totals, including shipping and taxes, to provide customers with complete pricing information.
- The cart should integrate with product pages and inventory systems to ensure accuracy and efficiency.
Payment Gateway Integrations
Secure and versatile payment solutions are non-negotiable:
- The site should offer multiple payment methods, from credit cards to digital wallets, catering to a wide range of customer preferences.
- Payment gateways must encrypt data to protect sensitive financial information during transactions.
- Adherence to the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is essential for any e-commerce platform.
Security
Robust security measures are paramount:
- Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certification ensures that all data passed between the web server and browsers remain private.
- Implementing strong data protection protocols to safeguard user information against breaches.
- Security systems must be regularly updated to defend against the latest cyber threats.
SEO
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is vital for visibility:
- Product descriptions, titles, and metadata should be optimized with relevant keywords to improve search rankings.
- With the increasing prevalence of mobile shopping, sites must be responsive and mobile-friendly.
- High-quality, original content not only aids SEO but also enhances user engagement.
User Experience (UX)
The UX should be intuitive and straightforward:
- A clear, logical navigation structure helps users find what they need without frustration.
- Pages should load quickly to reduce bounce rates and improve overall satisfaction.
- The site must be accessible to users with disabilities, complying with the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG).
Customer Service
Exceptional customer service is a must:
- Offering support through various channels, including live chat, email, and phone.
- Providing FAQs and help sections for customers who prefer to find answers independently.
- Implementing systems for customers to leave feedback can help improve the service and product offerings.
Analytics and Reporting
Data is key to understanding customers:
- Understanding where visitors come from and how they interact with the site.
- Detailed reports on sales performance help in making informed business decisions.
- Analyzing customer behavior to tailor the shopping experience and increase conversion rates.
How do E-commerce Websites Make Money?

E-commerce websites generate revenue through various business models and strategies. Here are some of the most common ways:
1. Sales Revenue Model
The most traditional method, e-commerce websites make money by selling products or services directly to consumers or other businesses. This can include manufacturers selling their own products, distributors selling to wholesalers, or retailers selling to the general public.
2. Subscription Revenue Model
Websites like Amazon Prime and Netflix have popularized the subscription model, where users pay a recurring fee to access products or services. This model provides a steady stream of income and can be applied to various industries, from media to software and consumer goods.
3. Marketplace Model
Platforms such as Amazon and eBay operate on a marketplace model, connecting buyers and sellers and facilitating transactions. They may charge sellers a subscription fee, a commission on each sale, or both.
4. Advertising Model
E-commerce sites with high traffic can earn significant revenue by displaying third-party ads. This includes selling ad spaces directly to advertisers or using programs like Google AdSense for targeted advertising.
5. Affiliate and Commission-Based Models
E-commerce websites can partner with other businesses and promote their products or services. In return, they earn a commission for every sale made through their referral. Amazon’s affiliate program is a prime example of this model.
6. Data Selling
E-commerce websites collect vast amounts of customer data. While ethical considerations are paramount, anonymized data can be sold to market research companies interested in consumer behavior. This should be done with user consent and in compliance with data protection laws.
7. Transaction Fee Model
Some e-commerce platforms, like Etsy and eBay, host third-party sellers. These platforms make money by charging a fee for every transaction made on their site.
8. Dropshipping and White-Labeling
Dropshipping allows e-commerce websites to sell products without holding inventory, as items are shipped directly from the supplier to the customer
. White-labeling involves selling products produced by another company under the e-commerce brand’s label
These seven revenue streams, either used alone or in combination, can turn a profit for e-commerce websites.
What are the Benefits of Using Ecommerce Sites?
Ecommerce sites offer a multitude of advantages for both businesses and consumers. Here are some of the key benefits:
1. Convenience and Accessibility
One of the most significant benefits of e-commerce sites is the convenience they offer. Unlike traditional brick-and-mortar stores that operate within fixed hours, e-commerce sites are accessible 24/7. This means that customers can shop at their own pace and at a time that suits them best. Whether it’s a late-night impulse buy or an early morning grocery order, e-commerce sites cater to the needs of all customers, irrespective of their schedules.
2. Wide Range of Products
E-commerce sites often have a vast product range, offering a variety of goods from different brands. For instance, a customer looking for a specific brand of sneakers would have to visit multiple physical stores before finding the right one. However, on an e-commerce site, they can find numerous brands and models all in one place. This not only saves time but also allows customers to compare different products easily.
3. Elimination of Middlemen
One of the main benefits of ecommerce is the absence of middlemen. This reduces the cost price to a greater degree and establishes a direct link between buyer and seller.
4. Easy Price Comparison
Another significant advantage of e-commerce sites is the ease of price comparison. Customers can compare prices of the same product from different sellers with just a few clicks. This transparency in pricing helps customers make informed decisions and ensures they get the best value for their money. For example, if a customer is looking to buy a laptop, they can quickly check the prices offered by different sellers on the e-commerce platform and choose the one that offers the best deal.
5. Detailed Product Information
E-commerce websites provide comprehensive information about the products they sell. This includes detailed product specifications, customer reviews, and ratings. For instance, if a customer is interested in buying a smartphone, they can find all the necessary information about its features, performance, and user experience on the e-commerce site. This wealth of information helps customers make informed purchasing decisions.
6. Global Access
E-commerce breaks down geographical barriers, allowing customers to purchase products from any part of the world. A customer in the US can purchase a unique handcrafted item from a seller in India through an e-commerce site.
7. Personalized Shopping Experience
E-commerce sites use algorithms to understand customer preferences and shopping habits. This allows them to offer a personalized shopping experience. For instance, if a customer frequently purchases books from a particular genre, the e-commerce site can recommend similar books that the customer might like. This personalized shopping experience makes online shopping more enjoyable and efficient.
8. Easy Returns and Refunds
Many e-commerce sites offer easy return and refund policies. This reduces the risk associated with online shopping. If a product does not meet a customer’s expectations, they can easily return it and get a refund. For example, if a customer purchases a dress that doesn’t fit well, they can return it to the e-commerce site and get their money back. This ease of returns and refunds makes online shopping a safer option for customers.
What are the Challenges of Ecommerce Sites?
While e-commerce sites offer numerous advantages, they also face a unique set of challenges. Let’s take a deeper look at these hurdles.
1. Security Concerns
Ecommerce sites handle sensitive customer information, making them attractive targets for cybercriminals. With increasing cyber threats, e-commerce sites have to invest heavily in robust security measures to protect customer data and maintain trust.
2. High Competition
The e-commerce market is highly competitive, with numerous players vying for customer attention. Standing out among competitors requires strategic pricing, unique product offerings, and exceptional customer service.
3. Customer Trust
Building customer trust is a significant challenge for e-commerce sites. Since customers cannot physically inspect products before making a purchase, they often have concerns about the quality and authenticity of products. Detailed product descriptions, high-quality images, customer reviews, and easy return policies can help alleviate these concerns.
4. Shipping and Logistical Issues
E-commerce sites need to manage complex logistics, including inventory management, packaging, shipping, and delivery. Shipping delays, high shipping costs, and damaged goods can lead to customer dissatisfaction.
5. Website Performance
The performance of the e-commerce site itself is crucial. Slow loading times, complicated navigation, and poor user experience can drive customers away. E-commerce sites must continuously optimize their website performance to provide a seamless shopping experience.
6. International Regulations
For e-commerce sites that ship internationally, navigating the different tax laws, import regulations, and shipping restrictions of each country can be challenging.
7. Customer Retention
With so many options available, retaining customers can be a challenge for e-commerce sites. They need to provide excellent customer service, personalized shopping experiences, and loyalty programs to encourage repeat purchases.
How Can You Start a Successful E-commerce Site?

Starting a successful ecommerce site involves several critical steps, each of which requires careful consideration and strategic planning:
1. Figure Out What You’re Going to Sell
Before anything else, identify the products or services you plan to offer. Consider your interests, passions, and select an eCommerce niche that is both desirable and viable. Conduct thorough market research to understand customer needs and analyze your competitors to find your unique selling proposition.
2. Determine your ecommerce business model
As discussed earlier in this guide, an e-commerce business can utilize a variety of business models (B2B, B2C, C2C, and C2B, etc.). The model you choose determines who you will be selling your products or services to. Select the model that best suits your product, market, and cost structure.
3. Choose Domain Name
Your domain name is your online identity, so select one that is short, memorable, and reflective of your brand. Avoid hyphens and numbers, and consider including relevant keywords to improve SEO. A .com domain is often preferred for its memorability and credibility. Some of the top domain registration services include GoDaddy, Namecheap, and Google Domains.
4. Pick Your Ecommerce Platform
Choose a CMS or e-commerce platform that matches your technical skills and meets your business needs. Some popular e-commerce platforms are Shopify, Magento (Adobe Commerce), WooCommerce, and BigCommerce. These platforms offer a range of features that can help you manage your business as it grows and evolves. Similarly, for hosting services, consider reputable providers like Bluehost, Hostinger, SiteGround, DreamHost, and GoDaddy Hosting.
5. Choose and Customize Your Template
Pick a theme or template that aligns with your brand’s aesthetic and offers a user-friendly experience. Customization is key to standing out, so tailor your site’s design to create a unique and engaging customer experience. Platforms like Shopify and Wix offer a wide range of customizable templates.
6. Finalize Your Product Marketing
Develop a comprehensive marketing strategy that includes product descriptions, high-quality images, and SEO optimization. Utilize various channels to reach your target audience.
Your marketing plan can include introducing a loyalty program, creating an email win-back campaign, offering email or SMS sign-up coupons, releasing new items on a schedule, building a subscription model, and perfecting the cross-sell and upsell. Tools like Mailchimp for email marketing and Hootsuite for social media management can be very helpful.
7. Setup Payments and Checkout
Implement a secure and efficient payment gateway to facilitate transactions. Offer multiple payment options to cater to customer preferences and ensure a smooth checkout process to reduce cart abandonment. Payment gateways like PayPal, Stripe, and Square are widely used and trusted.
8. Setup Shipping and Delivery
Determine your shipping strategy, including carriers, shipping rates, delivery times and return policies. Provide clear information to customers and consider offering free shipping to increase competitiveness. Shipping solutions like ShipStation or Shippo can streamline this process.
9. Market Your Online Store and Sell
Invest in marketing to drive traffic to your online store, convert that traffic into paying customers, and retain those customers post-purchase. This can include social media marketing, email marketing, SEO optimizations, special promotions, pay-per-click (PPC) advertising, and optimizing product listings with high-quality images. SEO tools like SEMrush and Moz can help optimize your site for search engines.
Throughout each step, focus on creating a mobile-friendly experience, as a significant portion of online shopping is done on mobile devices. Track analytics to fine-tune your strategy and encourage customer feedback to improve your offerings.
How Can You Track the Success of Your E-commerce Website?
Tracking the success of your ecommerce website helps in understanding customer behavior, optimizing your sales funnel, and ultimately driving revenue growth. Here are the key metrics and tools you should use to monitor your online store’s performance effectively:
1. Monitor Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
KPIs are quantifiable measurements that help you assess the performance of your ecommerce website. Some of the important KPIs to track include:
- Conversion Rate: This is the percentage of visitors who make a purchase. A healthy conversion rate indicates that your site is effective at converting traffic into sales.
- Average Order Value (AOV): AOV tracks the average dollar amount spent each time a customer places an order. To increase AOV, consider upselling or cross-selling strategies.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): CLV predicts the net profit attributed to the entire future relationship with a customer. Understanding CLV helps tailor customer retention strategies.
- Traffic (Unique Visitors): Monitor the number of unique visitors to gauge brand reach and the effectiveness of marketing campaigns.
- Bounce Rate: This shows the percentage of visitors who navigate away from your site after viewing only one page.
- Cart Abandonment Rate: This metric shows the percentage of shoppers who add items to their cart but do not complete the purchase. A high rate may indicate issues with the checkout process.
- Return on Investment (ROI): ROI measures the profitability of your marketing efforts. It helps you understand which campaigns are working and which are not.
2. Use Ecommerce Analytics Tools
Several ecommerce analytics tools can help you track mentioned KPIs and provide valuable insights into your website’s performance. Here are some recommended tools:
- Google Analytics: The most widely used web analytics service, Google Analytics offers insights into traffic sources, user behavior, and conversion data.
- Heatmap Tools (e.g., Hotjar, Crazy Egg): These tools provide visual representations of where users click, move, and scroll on your site, helping you understand user engagement.
- SEO Tools (e.g., SEMrush, Ahrefs): Use these tools to track your search engine rankings and identify opportunities to improve your site’s visibility.
- Social Media Analytics: Platforms like Facebook Insights and Twitter Analytics can help you track engagement and the effectiveness of your social media campaigns.
- Email Marketing Analytics: Services like Mailchimp and Constant Contact offer detailed reports on open rates, click-through rates, and conversions from email campaigns.
3. Regularly Review and Adjust Your Strategies
Regularly reviewing your KPIs and adjusting your strategies accordingly can help you optimize your website’s performance and boost your e-commerce success. For example, if your cart abandonment rate is high, you might need to simplify your checkout process or offer more payment options.
Here are a few recommendations:
- Regularly review your KPIs to understand the health of your ecommerce business.
- Use A/B testing to optimize your website and improve conversion rates.
- Implement SEO best practices to enhance organic traffic.
- Continuously gather and act on customer feedback to refine the user experience.
Dealing with the complexities of an e-commerce website can be difficult. From setting up your online store to optimizing for conversions, the process requires more than just understanding the technical aspects. But you don’t have to do it alone. Aureate Labs offers top-tier e-commerce development and consultation services tailored to your needs. Contact us today, and let’s turn these challenges into opportunities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an example of e-commerce website?
Amazon.com Inc. is a prime example of a successful e-commerce business. Other examples include Zulu Longines, Potion, Help Scout, and Bite Toothpaste Bits.
Which is the best platform to create an eCommerce website?
The best platform for creating an ecommerce website depends on your specific needs and technical skills. However, Shopify is often recommended for its all-in-one e-commerce and retail platform features. Other notable platforms include Wix, Squarespace, BigCommerce, and WooCommerce.
Is eCommerce still growing?
Yes, e-commerce is still growing. The global e-commerce growth rate for 2026 is forecast at 7.5%, bringing global e-commerce sales worldwide to $6.3 trillion. E-commerce growth rate worldwide is expected to continue at a relatively steady pace.
How much an e-commerce website cost?
The cost of an e-commerce website can vary widely. For small businesses with a limited product range, costs can be a few hundred dollars or less, while larger businesses with extensive catalogs may require a more significant investment.
Here’s a rough breakdown of major costs:
- Domain registration ($10 to $30 annually)
- Web hosting ($2 to $250 monthly)
- SSL certificate ($0 to $1000 yearly)
- E-commerce platform ($20 to $300 based on plan & features)
- Website design and development ($60 to $10000)
and Additional costs like payment gateway fees, digital marketing, and website maintenance.
Can I build my own e-commerce website?
Yes, you can build your own e-commerce website using platforms like WordPress, Shopify, or Wix. These offer easy-to-use templates. However, managing complex e-commerce features may require some technical expertise.






Post a Comment
Got a question? Have a feedback? Please feel free to leave your ideas, opinions, and questions in the comments section of our post! ❤️